3.5 KiB
ZipPy: Fast method to classify text as AI or human-generated
This is a research repo for fast AI detection using compression. While there are a number of existing LLM detection systems, they all use a large model trained on either an LLM or its training data to calculate the probability of each word given the preceeding, then calculating a score where the more high-probability tokens are more likely to be AI-originated. Techniques and tools in this repo are looking for faster approximation to be embeddable and more scalable.
Compression-based detector (zippy.py and nlzmadetect)
ZipPy uses either the LZMA or zlib compression ratios as a way to indirectly measure the perplexity of a text.
Compression ratios have been used in the past to detect anomalies in network data
for intrusion detection, so if perplexity is roughly a measure of anomalous tokens, it may be possible to use compression to detect low-perplexity text.
LZMA and zlib creates a dictionary of seen tokens, and then uses though in place of future tokens. The dictionary size, token length, etc.
are all dynamic (though influenced by the 'preset' of 0-9--with 0 being the fastest but worse compression than 9). The basic idea
is to 'seed' a compression stream with a corpus of AI-generated text (ai-generated.txt) and then measure the compression ratio of
just the seed data with that of the sample appended. Samples that follow more closely in word choice, structure, etc. will acheive a higher
compression ratio due to the prevalence of similar tokens in the dictionary, novel words, structures, etc. will appear anomalous to the seeded
dictionary, resulting in a worse compression ratio.
Current evaluation
Some of the leading LLM detection tools are:
OpenAI's model detector (v2), Content at Scale, GPTZero, CrossPlag's AI detector, and Roberta.
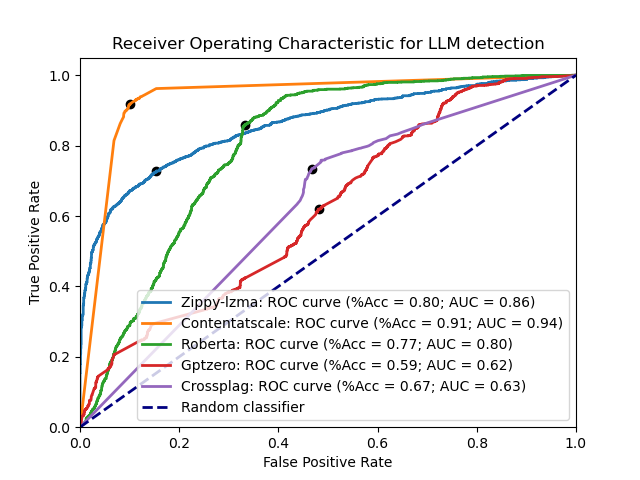
Here are each of them compared with both the LZMA and zlib detector across the test datasets:
Usage
ZipPy will read files passed as command-line arguments, or will read from stdin to allow for piping of text to it.
$ python3 zippy.py -h
usage: zippy.py [-h] [-p P] [-e {zlib,lzma,brotli,ensemble}] [-s | sample_files ...]
positional arguments:
sample_files Text file(s) containing the sample to classify
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p P Preset to use with compressor, higher values are slower but provide better compression
-e {zlib,lzma,brotli,ensemble}
Which compression engine to use: lzma, zlib, brotli, or an ensemble of all engines
-s Read from stdin until EOF is reached instead of from a file
$ python3 zippy.py samples/human-generated/about_me.txt
samples/human-generated/about_me.txt
('Human', 0.06013429262166636)
If you want to use the ZipPy technology in your browser, check out the Chrome extension or the Firefox extension that runs ZipPy in-browser to flag potentially AI-generated content.