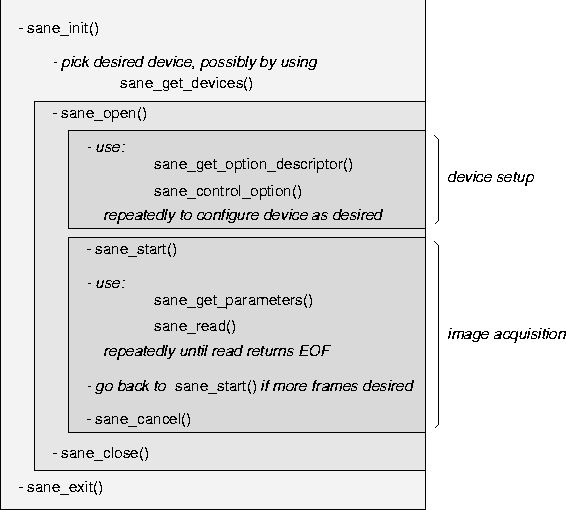
The code flow for the SANE API is illustrated in Figure 4. Functions sane_init() and sane_exit() initialize and exit the backend, respectively. All other calls must be performed after initialization and before exiting the backend.

Function sane_get_devices() can be called any time after sane_init() has been called. It returns the list of the devices that are known at the time of the call. This list may change over time since some devices may be turned on or off or a remote host may boot or shutdown between different calls. It should be noted that this operation may be relatively slow since it requires contacting all configured devices (some of which may be on remote hosts). A frontend may therefore want to provide the ability for a user to directly select a desired device without requiring a call to this function.
Once a device has been chosen, it is opened using a call to sane_open(). Multiple devices can be open at any given time. A SANE backend must not impose artificial constraints on how many devices can be open at any given time.
An opened device can be setup through the corresponding device handle using functions sane_get_option_descriptor() and sane_control_option(). While setting up a device, obtaining option descriptors and setting and reading of option values can be mixed freely. It is typical for a frontend to read out all available options at the beginning and then build a dialog (either graphical or a command-line oriented option list) that allows to control the available options. It should be noted that the number of options is fixed for a given handle. However, as options are set, other options may become active or inactive or their constraint may change. Thus, after setting an option, it may be necessary to re-read the descriptors. While setting up the device, it is also admissible to call sane_get_parameters() to get an estimate of what the image parameters will look like once image acquisition begins.
The device handle can be put in blocking or non-blocking mode by a call to sane_set_io_mode(). Devices are required to support blocking mode (which is the default mode), but support for non-blocking I/O is strongly encouraged for operating systems such as UNIX.
After the device is setup properly, image acquisition can be started by a call to sane_start(). The backend calculates the exact image parameters at this point. So future calls to sane_get_parameters() will return the exact values, rather than estimates. Whether the physical image acquisition starts at this point or during the first call to sane_read() is unspecified by the SANE API. If non-blocking I/O and/or a select-style interface is desired, the frontend may attempt to call sane_set_io_mode() and/or sane_get_select_fd() at this point. Either of these functions may fail if the backend does not support the requested operation.
Image data is collected by repeatedly calling sane_read()
until this function will return an end-of-file status
(SANE_STATUS_EOF). This indicates the end of the current
frame. If the frontend expects additional frames (e.g., the
individual channels of a red/green/blue image or multiple images),
it can call sane_start() again.
If the SANE_PFLAG_LAST_FRAME bit is set in flags, the
current image is complete. In this case, it should be tested, if
flags has the SANE_PFLAG_MORE_IMAGES bit set.
If yes, further calls to sane_start() can be made to acquire
more images. Please note, that as this bit has to be set at the beginning
of a the transmission of the last frame before the new image, it is possible,
that no reliable decision can be made at this time. It is thus permissible
for a backend to set this bit, and then later at the actual call to
sane_start() return an error like SANE_STATUS_NO_DOCS.
Such a sequence is permitted to transmit multiple images from a single
page as well as multiple pages. This behaviour should be controlled by
backend options as required, to allow single-page scanning as well as
ADF-batch-scanning. The frontend should always continue reading all images
until a frame with SANE_PFLAG_LAST_FRAME on
and SANE_PFLAG_MORE_IMAGES off is encountered, or an error other
than SANE_STATUS_EOF occurs in a SANE function.
Note that SANE_STATUS_NO_DOCS also is an allowed way for the backend
to indicate the end of a multiple image scan.
A frontend may choose to skip frames (e.g. because it cannot parse them),
which is accomplished by simply calling sane_start again, which will get
you to the next frame, without having to read and discard the current one.
In order to prematurely stop scanning and to reset the backend state,
sane_cancel() can be called at any time. This call is required
as well after normal termination of a multiple image scan as described above.
When done using the device, the handle should be closed by a call to sane_close(). Finally, before exiting the application, function sane_exit() must be called. It is important not to forget to call this function since otherwise some resources (e.g., temporary files or locks) may remain unclaimed.
The following C sample code implements a reference loop for acquiring
multiple images:
SANE_Parameters parms;
SANE_Status status;
do
{
do
{
/* Now start acquiring the next frame. */
status = sane_start (handle);
/* if that failed, we have a problem, and no more frames can be
* read at this time. Due to SANE_PFLAG_MORE_IMAGES still
* being clear, this will break out of _BOTH_ loops.
*/
if (status != SANE_STATUS_GOOD)
break;
/* Now let us see what the next frame brings. */
status = sane_get_parameters (handle, &parms);
/* This actually should not fail, but maybe the doc feeder
* jammed or something, so we break as well, if something
* is wrong.
*/
if (status != SANE_STATUS_GOOD)
break;
/* Now we check the announced parameters, if we can make use
* of the frame data. If not, we skip over to the next frame.
*/
if (do_i_like_that (&parms) == NO)
continue;
/* Set up for reading the data here. Mangle filenames,
* allocate memory, rewind multiframe files, ask user
* for confirmation, ...
*/
setup_for_transfer (...);
/* Now we read in the frame data and process it. This should
* return SANE_STATUS_GOOD, until the frame is complete,
* what causes SANE_STATUS_EOF to be returned.
*/
while (SANE_STATUS_GOOD == (status = sane_read (...)))
read_in_and_process_data_as_required ();
/* If transfer was broken due to anything but EOF, break out. */
if (status != SANE_STATUS_EOF)
break;
/* Now loop until we have all frames of an image. */
}
while (!(parms.flag & SANE_PFLAG_LAST_FRAME));
/* O.K. - we now have a complete image. Fit it together, save it,
* flush buffers, transmit it, increment filenames, etc.
*/
/* Now check for more pending images. If we have more, redo from start.
* Some backends might cheat here and send us for an extra round which
* will fail at sane_start, as they were not able to determine if they
* would have more data at the start of the last frame we read.
*/
}
while (parms.flags & SANE_PFLAG_MORE_IMAGES);
/* No more data. Fine. Reset the backend and go back to option-control
* loop.
*/
sane_cancel (handle);