5.1 KiB
XGBoost
XGBoost is an implementation of gradient boosted decision trees designed for speed and performance.
Introduction to Gradient Boosting
Gradient boosting is a powerful technique for building predictive models that has seen widespread success in various applications.
- Boosting Concept: Boosting originated from the idea of modifying weak learners to improve their predictive capability.
- AdaBoost: The first successful boosting algorithm was Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost), which utilizes decision stumps as weak learners.
- Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM): AdaBoost and related algorithms were later reformulated as Gradient Boosting Machines, casting boosting as a numerical optimization problem.
- Algorithm Elements:
- Loss function: Determines the objective to minimize (e.g., cross-entropy for classification, mean squared error for regression).
- Weak learner: Typically, decision trees are used as weak learners.
- Additive model: New weak learners are added iteratively to minimize the loss function, correcting the errors of previous models.
Introduction to XGBoost
- eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XBGoost): a more regularized form of Gradient Boosting, as it uses advanced regularization (L1&L2), improving the model’s generalization capabilities.
- It’s suitable when there is a large number of training samples and a small number of features; or when there is a mixture of categorical and numerical features.
- Development: Created by Tianqi Chen, XGBoost is designed for computational speed and model performance.
- Key Features:
- Speed: Achieved through careful engineering, including parallelization of tree construction, distributed computing, and cache optimization.
- Support for Variations: XGBoost supports various techniques and optimizations.
- Out-of-Core Computing: Can handle very large datasets that don't fit into memory.
- Advantages:
- Sparse Optimization: Suitable for datasets with many zero values.
- Regularization: Implements advanced regularization techniques (L1 and L2), enhancing generalization capabilities.
- Parallel Training: Utilizes all CPU cores during training for faster processing.
- Multiple Loss Functions: Supports different loss functions based on the problem type.
- Bagging and Early Stopping: Additional techniques for improving performance and efficiency.
- Pre-Sorted Decision Tree Algorithm:
- Features are pre-sorted by their values.
- Traversing segmentation points involves finding the best split point on a feature with a cost of O(#data).
- Data is split into left and right child nodes after finding the split point.
- Pre-sorting allows for accurate split point determination.
- Limitations:
- Iterative Traversal: Each iteration requires traversing the entire training data multiple times.
- Memory Consumption: Loading the entire training data into memory limits size, while not loading it leads to time-consuming read/write operations.
- Space Consumption: Pre-sorting consumes space, storing feature sorting results and split gain calculations.
XGBoosting: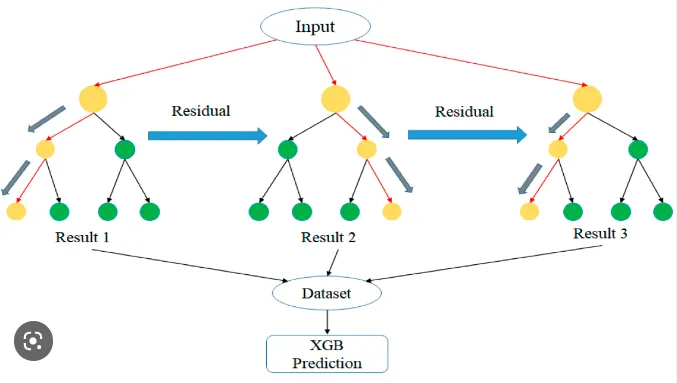
Develop Your First XGBoost Model
This code uses the XGBoost library to train a model on the Iris dataset, splitting the data, setting hyperparameters, training the model, making predictions, and evaluating accuracy, achieving an accuracy score of X on the testing set.
# XGBoost with Iris Dataset
# Importing necessary libraries
import numpy as np
import xgboost as xgb
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Loading a sample dataset (Iris dataset)
data = load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
# Splitting the dataset into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Converting the dataset into DMatrix format
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, label=y_train)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test, label=y_test)
# Setting hyperparameters for XGBoost
params = {
'max_depth': 3,
'eta': 0.1,
'objective': 'multi:softmax',
'num_class': 3
}
# Training the XGBoost model
num_round = 50
model = xgb.train(params, dtrain, num_round)
# Making predictions on the testing set
y_pred = model.predict(dtest)
# Evaluating the model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
Output
Accuracy: 1.0
Conclusion
XGBoost's focus on speed, performance, and scalability has made it one of the most widely used and powerful predictive modeling algorithms available. Its ability to handle large datasets efficiently, along with its advanced features and optimizations, makes it a valuable tool in machine learning and data science.