kopia lustrzana https://github.com/kartoza/docker-osm
339 wiersze
14 KiB
Markdown
339 wiersze
14 KiB
Markdown
# Docker-OSM
|
|
|
|
A docker compose project to setup an OSM PostGIS database with automatic
|
|
updates from OSM periodically.
|
|
The only files you need is a PBF file, geojson (if you intend to restrict data download to
|
|
a smaller extent than the one specified by the PBF) and run the docker compose project.
|
|
|
|
## General architecture
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
## Quick setup
|
|
|
|
As a quick example, we are going to setup Docker-OSM with default values everywhere:
|
|
* Download a PBF file from http://download.geofabrik.de/
|
|
* Put the file in the `settings` folder and rename it `country.pbf`.
|
|
|
|
Alternatively you can execute the `settings_downloader.sh` script to download the pbf and the clip file
|
|
```bash
|
|
bash ./settings_downloader.sh GEOJSON_URL CONTINENT COUNTRY ie
|
|
bash ./settings_downloader.sh https://github.com/kartoza/docker-osm/raw/develop/settings/clip.geojson africa south-africa
|
|
```
|
|
For a full list of allowed file names read json file `countries.json`
|
|
|
|
Alternatively you can use the python script `pbf_downloader.py`
|
|
|
|
For local usage, the containers are set up using docker-compose configuration. The configuration files consists of
|
|
two sets of config file. The first one is `.env` which contains lists of environment variables.
|
|
Copy the `.env` file from the `.example.env` in this repo.
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
cp .example.env .env
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For subsequent configuration, edit the `.env` files to tweak your options.
|
|
|
|
The second set of configuration is using a `docker-compose.yml` files, which is a compose files docker-compose is using.
|
|
|
|
For minimum set of production environment, the configuration file is described in `docker-compose.yml` file.
|
|
The other YAML files with prefix `docker-compose` is a configuration file that you can merge with the basic `docker-compose.yml` file. To use more than one configuration file, you edit `.env` file and change the `COMPOSE_FILE` variable to include all
|
|
the compose file you desired, separated by a colon `:` for each file.
|
|
|
|
For example, by default, the example file is using both `docker-compose.yml` and `docker-compose.develop.yml` because
|
|
we expect you to provide the necessary settings in `settings` folder. Thus the `COMPOSE_FILE` variable looks like this:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
COMPOSE_FILE=docker-compose.yml:docker-compose.develop.yml
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
In production environment, normally all the persistent data is stored in a volume, instead of bind mounted.
|
|
In this case only the `docker-compose.yml` is enough, and you need to provide the settings inside the volume itself.
|
|
|
|
To build the image yourself, include the `docker-compose.build.yml` file.
|
|
|
|
To use helper services such as pgadmin, include `docker-compose.pgadmin.yml`, and `docker-compose.web.yml` for web demo.
|
|
|
|
If you are familiar with how docker-compose work, you can also use a standard convention by putting `docker-compose.override.yml`
|
|
file and include it in the `COMPOSE_FILE` variable.
|
|
|
|
To store the configuration for long-term use (for archiving or diffing of different configuration). You can interpolate the
|
|
current variables in `.env` and generate a full config files:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
docker-compose config > docker-compose.production.yml
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The above command will include and merged all your config files specified in `COMPOSE_FILE` variable and also fill out the
|
|
variables parameterized in the docker-compose file.
|
|
|
|
* If you want to connect from your local QGIS Desktop:
|
|
* In the file `docker-compose.yml`, uncomment the block:
|
|
|
|
```yml
|
|
# Uncomment to use the postgis database from outside the docker network
|
|
ports:
|
|
- "35432:5432"
|
|
```
|
|
* Do `make run` in the build directory. This will download and execute the docker-osm project.
|
|
It might be very long depending of your bandwidth and the PBF you are importing.
|
|
* In QGIS, add a new PostGIS connection: `localhost`, database `gis`, port `35432`, `docker` for both username and password.
|
|
* That's it! You have an OSM database, up and running. The update is done every 2 minutes from the main OSM website.
|
|
|
|
For further reading and customizations, read below.
|
|
|
|
## Docker cloud
|
|
|
|
Dockerfiles are executed on [Docker Cloud kartoza/docker-osm](https://cloud.docker.com/swarm/kartoza/repository/docker/kartoza/docker-osm/general)
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
docker pull kartoza/docker-osm:imposm-latest
|
|
docker pull kartoza/docker-osm:osmupdate-latest
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
To run you can use the provided docker-compose project and use the images
|
|
hosted on the internet. This is useful if you want to integrate Docker-OSM in
|
|
your existing docker-compose project.
|
|
|
|
## Usage
|
|
|
|
### PBF File
|
|
In this example we will set up an OSM database for South Africa that
|
|
will pull for updates every 2 minutes.
|
|
|
|
Specify a PBF file for your area in the environment variables for `osm_downloader` container.
|
|
You can download some PBF files on these URLS for instance :
|
|
* http://download.geofabrik.de/
|
|
* http://download.openstreetmap.fr/extracts/
|
|
|
|
|
|
You must put only one PBF file in the settings folder. Only the last one will be read.
|
|
|
|
### OSM Features
|
|
|
|
In `settings`, you can edit the `mapping.yml` to customize the PostGIS schema.
|
|
You can find the documentation about the mapping configuration on the imposm
|
|
website: https://imposm.org/docs/imposm3/latest/mapping.html
|
|
The default file in Docker-OSM is coming from
|
|
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/omniscale/imposm3/master/example-mapping.yml
|
|
|
|
**Note** Imposm is designed for spatial analysis, not for OSM contribution analysis.
|
|
If you need such a feature, you need to use another database schema supporting OSM Metadata.
|
|
You can check the [OSM Wiki](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Databases_and_data_access_APIs#Database_Schemas) for "Lossless" schemas.
|
|
|
|
### Updates
|
|
|
|
You can configure the time interval in the docker-compose file. By default,
|
|
it's two minutes. If you set the TIME variable to 0, no diff files will be
|
|
imported.
|
|
|
|
The default update stream is worldwide. So even if you imported a local PBF, if
|
|
you don't set a clipping area, you will end with data from all over the world.
|
|
|
|
### Clipping
|
|
|
|
During the initial import or post update imposm uses the flag `-limito` which allows
|
|
you to define a smaller area that you can work with.
|
|
This is always desirable to limit the features being imported into the database rather
|
|
than clipping them.
|
|
|
|
**NB:** Ensure you add a geojson covering the area you intend to clip into the `settings` folder.
|
|
The geojson can be the same extent of the administrative area for your country, or it can be a
|
|
smaller extent. The CRS of the geojson should always be EPSG:4326.
|
|
|
|
|
|
**NB:** It is encouraged to simplify the geometry for the `clip.geojson` as
|
|
a simplified geometry is easier to process during the import.
|
|
Rather use the minimum bounding box for the area you intend to clip your dataset with.
|
|
|
|
### QGIS project
|
|
|
|
There is a default QGIS project provided in the `web/` folder, named `osm_mirror_qgis_project.qgz`. To be able to load the layers in this project correctly in QGIS, first run `make materialized_views` and `make elevation` then set up your connection service file with the following parameters. The host parameter is where you have set up `docker-osm`:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
[docker-osm]
|
|
dbname=gis
|
|
port=35432
|
|
user=docker
|
|
password=docker
|
|
host=<host>
|
|
sslmode=disable
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### QGIS Styles
|
|
|
|
The database is provided with some default styles. These styles will be loaded
|
|
automatically when loaded in QGIS. It's following the default OSM mapping from
|
|
ImpOSM.
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
make import_styles
|
|
make remove_styles
|
|
make backup_styles
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### SQL Trigger, functions, views...
|
|
|
|
You can add PostGIS functions, triggers, materialized views into an SQL file called `post-pbf-import.sql`.
|
|
It will be imported automatically in the database.
|
|
|
|
### Build and run
|
|
|
|
Now build the docker images needed to run the application:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
docker-compose build
|
|
docker-compose up
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
In production, you should daemonize the services when bringing them up:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
docker-compose up -d
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can check the timestamp of your database by reading the file :
|
|
``settings/timestamp.txt`` or you can use :
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
make timestamp
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Display
|
|
|
|
In the makefile, you can switch to another docker compose project.
|
|
The other one includes QGIS Server. When it's running, you should be able to
|
|
open, on the host(not in docker), the `index.html` file and see OSM and QGIS
|
|
Server showing PostGIS tables. The webpage is using Leaflet.
|
|
|
|
If you want to tweak the QGIS Project, you need to add a host in your in `/etc/hosts`:
|
|
```
|
|
127.0.0.1 db
|
|
```
|
|
Because in the docker-compose file, the link is made with the PostGIS database using the alias `db`.
|
|
|
|
## In the background
|
|
|
|
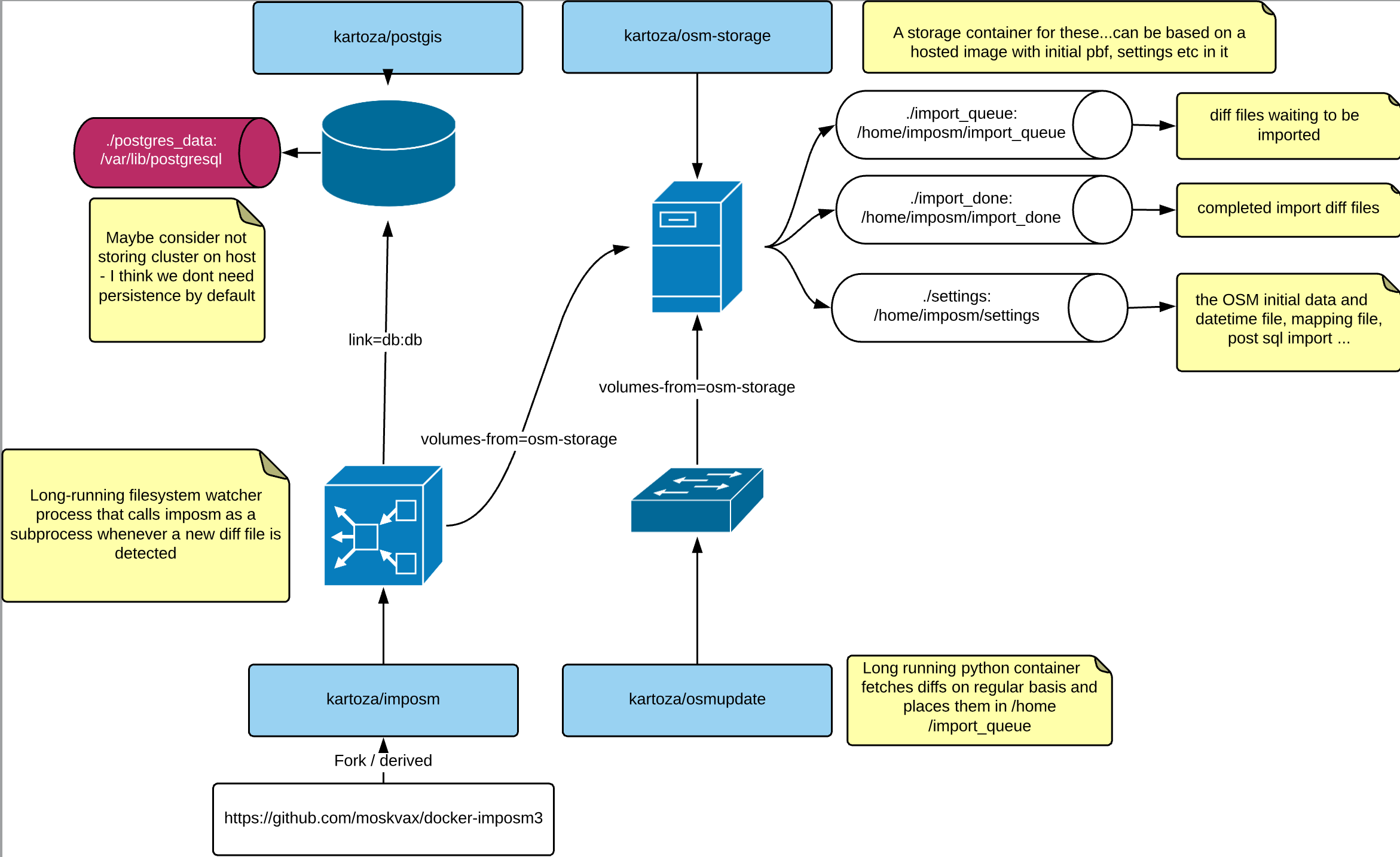
|
|
|
|
### Docker OSM Update
|
|
|
|
This docker image, when run will regularly fetch any new diff file for all the
|
|
changes that have happened in the world over the update interval.
|
|
|
|
You can also specify a custom url for fetching the diff if you wish to retrieve
|
|
regional diffs rather than the global one.
|
|
|
|
You can specify a polygonal area for the diff so that it will only apply features
|
|
from the diff that fall within that area. For example providing a polygon of the
|
|
borders of Malawi will result in only Malawi features being extracted from the diff.
|
|
|
|
**Note:** the diff retrieved and options specified here are not related to the
|
|
initial base map used - so for example if your initial base map is for Malawi and
|
|
you specify a diff area in Botswana, updated features in Botswana will be applied
|
|
to your base map which only includes features from Malawi. For this reason, take
|
|
care to ensure that your diff area coincides with the region covered by your
|
|
original base map.
|
|
|
|
Once the diff has been downloaded, it is placed into /home/import_queue where
|
|
it will be picked up by the long running imposm3 container, which will apply
|
|
the diff to the database.
|
|
|
|
You should have 3 folders : osm_pbf, import_queue, import_done
|
|
|
|
Put a state file in base-pbf like this one :
|
|
http://download.openstreetmap.fr/extracts/africa/south_africa.state.txt
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
docker build -t osmupdate .
|
|
docker run -v $('pwd')import-queue/:/home/import-queue -v $('pwd')base-pbf/:/home/base-pbf -v $('pwd')import-done/:/home/import-done -d osmupdate
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
With -e, you can add some settings :
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
- MAX_DAYS = 100, the maximum time range to assemble a cumulated changefile.
|
|
- DIFF = sporadic, osmupdate uses a combination of minutely, hourly and daily changefiles. This value can be minute, hour, day or sporadic.
|
|
- MAX_MERGE = 7, argument to determine the maximum number of parallely processed changefiles.
|
|
- COMPRESSION_LEVEL = 1, define level for gzip compression. values between 1 (low compression but fast) and 9 (high compression but slow)
|
|
- BASE_URL = http://planet.openstreetmap.org/replication/, change the URL to use a custom URL to fetch regional file updates.
|
|
- IMPORT_QUEUE = import_queue
|
|
- IMPORT_DONE = import_done
|
|
- OSM_PBF = osm_pbf
|
|
- TIME = 120, seconds between two executions of the script
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you are using docker-compose, you can use these settings within the
|
|
```docker-compose.yml``` file.
|
|
|
|
### Docker ImpOSM3
|
|
|
|
This image will take care of doing the initial load for the selected region
|
|
(e.g. planet, or a country such as Malawi) into your database. It will then
|
|
apply, at a regular interval (default is 2 minutes), any diff that arrives
|
|
in the /home/import_queue folder to the postgis OSM database. The diffs
|
|
are fetched by a separate container (see osm_update container).
|
|
|
|
The container will look for an OSM file (*.pbf) and its state file
|
|
(*.state.txt) in BASE_PBF.
|
|
|
|
With -e, you can add some settings :
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
- TIME = 120, seconds between 2 executions of the script
|
|
- POSTGRES_USER = docker, default user
|
|
- POSTGRES_PASS = docker, default password
|
|
- POSTGRES_HOST = db
|
|
- POSTGRES_PORT = 5432
|
|
- SETTINGS = settings, folder for settings (with *.json and *.sql)
|
|
- CACHE = cache, folder for caching
|
|
- BASE_PBF = base_pbf, folder the OSM file
|
|
- IMPORT_DONE = import_done, folder for diff which has been imported
|
|
- IMPORT_QUEUE = import_queue, folder for diff which hasn't been imported yet
|
|
- SRID = 4326, it can be 3857
|
|
- OPTIMIZE = false, check (Imposm)[http://imposm.org/docs/imposm3/latest/tutorial.html#optimize]
|
|
- DBSCHEMA_PRODUCTION = public, check (Imposm)[http://imposm.org/docs/imposm3/latest/tutorial.html#deploy-production-tables]
|
|
- DBSCHEMA_IMPORT = import, check (Imposm)[http://imposm.org/docs/imposm3/latest/tutorial.html#deploy-production-tables]
|
|
- DBSCHEMA_BACKUP = backup, check (Imposm)[http://imposm.org/docs/imposm3/latest/tutorial.html#deploy-production-tables]
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can adjust these preferences in the ```docker-compose.yml``` file provided
|
|
in this repository.
|
|
|
|
### Docker OSM Enrich
|
|
|
|
Docker osm-enrich is the extension for docker osm to get the changeset of the osm data.
|
|
It will get the data from osm API and also get the update data from files that generated from docker-osmupdate
|
|
|
|
- data is new (changeset is null) : get from docker osm
|
|
- data is exist but need to check the recent changeset : get data from file generated from osmupdate, update into database
|
|
|
|
osmenrich will create new fields which are:
|
|
- changeset_id
|
|
- changeset_timestamp
|
|
- changeset_version
|
|
- changeset_user
|
|
|
|
# PostGIS
|
|
|
|
For environment variables associated with `docker-postgis` refer to [docker postgis repository](https://github.com/kartoza/docker-postgis)
|
|
|
|
### Support
|
|
|
|
If you require more substantial assistance from [kartoza](https://kartoza.com) (because our work and interaction on docker-osm is pro bono),
|
|
please consider taking out a [Support Level Agreeement](https://kartoza.com/en/shop/product/support)
|
|
|
|
|
|
# Credits
|
|
|
|
This application was designed and implemented by:
|
|
|
|
* Etienne Trimaille (etienne.trimaille@gmail.com)
|
|
* Tim Sutton (tim@kartoza.com)
|
|
|
|
With some important design ideas provided by Ariel Nunez (ingenieroariel@gmail.com).
|
|
|
|
Parts of this project are built on the existing work of others.
|
|
|
|
July 2015
|