In detail: Reduced sample jitter by matching sampling rate to a multiple of OCR0A timer divider. Unit angle now configurable and scalable so that full precision (of integer range) can be used to calculate phase differences; the unit angle is configured to be an exact multiple of the samp$ Hilbert transformer fixed bug, simplified and improved in precision (improved from -15dB to -40dB in an image rejection setting). Arctan rounding errors reduced from approx. 5 degree to 0.8 degree. Moved from 8 bit to 16 bit precision for audio input and I/Q values. Microphone-input response now flat from 0-2200Hz (removed original high-pass filter with 20dB roll-off at 800Hz). Experimental code (currently commented-out) for measuring phase differences between programmatically synchronised SI5351 clocks. Fixed an issue where for every RX-TX transition a burst of random RF frequencies were emitted. Improved precision of smeter, and found that disabling smeter prevent spurs leaking in from LCD data transfer into RXi (smeter still enabled). Added a LUT-based pre-distortion algorithm that can be calibrated via an internal amplitude measurement. Fixed issue with the envelope generation through Q6 impacting the IMD-performance, dynamic range, efficiency and thermal-stability; this fix REQUIRES the removal of C31 and increase of C32 to$ Fixed an issue where VOX was unintentially triggering TX by ADC noise leaking through key-shaping circuit, and simplied VOX algorithm. Generaized PLL and MultiSynth algorithms and added experimental algorithm for setting a second frequency (via a different MS divider and where PLL is the same). Experimental code for measuring the phase of the transmitted signal (via PA and QSD), this could give insight in antenna impedance and PA phase-response as function of amplitude. |
||
|---|---|---|
| QCX-SSB.ino | ||
| README.md | ||
| layout.png | ||
| schematic.png | ||
README.md
ⓆⒸⓍ-ⓈⓈⒷ
QCX-SSB: SSB with your QCX transceiver (modification)
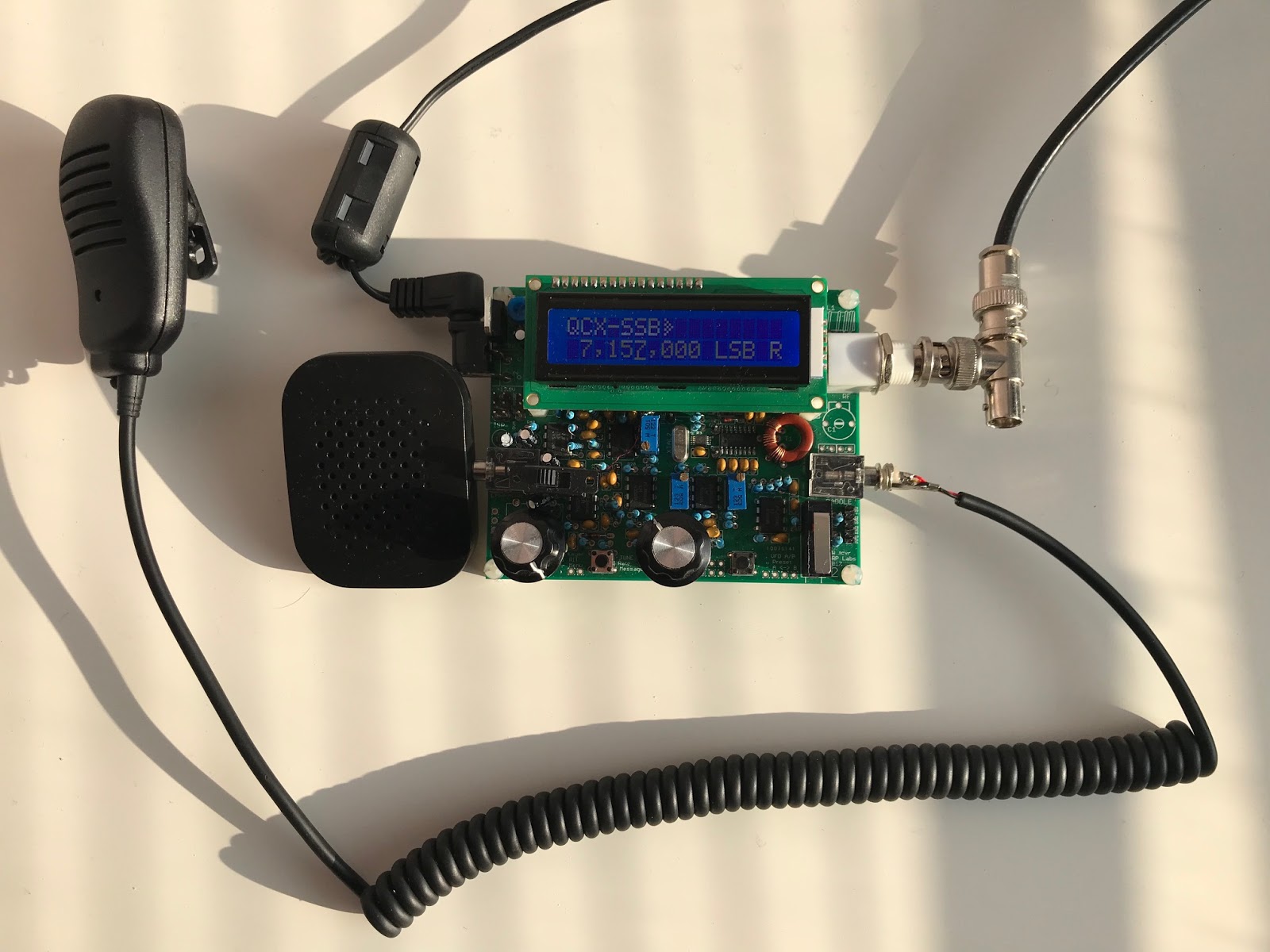
This is a simple and experimental modification that transforms a QCX into a (Class-E driven) SSB transceiver. It can be used to make QRP SSB contacts, or (in combination with a PC) used for the digital modes such as FT8. It can be fully-continuous tuned through bands 160m-10m in the LSB/USB-modes with a 2200Hz bandwidth has up to 5W PEP SSB output and features a software-based full Break-In VOX for fast RX/TX switching in voice and digital operations.
The SSB transmit-stage is implemented completely in a digital and software-based manner: at the heart the ATMEGA328P is sampling the input-audio and reconstructing a SSB-signal by controlling the SI5351 PLL phase (through tiny frequency changes over 800kbit/s I2C) and controlling the PA Power (through PWM on the key-shaping circuit). In this way a highly power-efficient class-E driven SSB-signal can be realized; a PWM driven class-E design keeps the SSB transceiver simple, tiny, cool, power-efficient and low-cost (ie. no need for power-inefficient and complex linear amplifier with bulky heat-sink as often is seen in SSB transceivers).
An Open Source Arduino sketch is used as the basis for the firmware, the hardware modification bypasses the QCX CW filter and adds a microphone input in-place of the DVM-circuit; the mod is easy to apply and consist of four wire and four component changes and after applying the transceiver remains compatible with the original QCX (CW) firmware.
This experiment is created to try out what can be done with minimal hardware; a simple ATMEGA processor, a QCX and a software-based SSB processing approach. It would be nice to add more features to the sketch, and try out if the QCX design can be further simplified e.g. by implementing parts of the receiver stage in software. Feel free to experiment with this sketch, let me know your thoughts or contribute here: https://github.com/threeme3/QCX-SSB There is a forum discussion on the topic here: QRPLabs Forum
73, Guido pe1nnz@amsat.org
List of features:
- EER/Polar-transmitter Class-E driven SSB transmit-stage
- Approximately 5W PEP SSB output (depending on supply voltage, PA voltage regulated through PWM with 36dB dynamic range)
- supports USB and LSB modes up to 2200 Hz bandwidth (receiver and transmitter)
- Receiver unwanted side-band rejection up to -20dB
- Continuously tunable through bands 80m-10m (anything between 20kHz-99MHz is tunable but with degraded or loss in performance)
- Multiband support 3
- Software-based VOX that can be used as fast Full Break-In (QSK operation) or assist in RX/TX switching for operating digital modes (no CAT or PTT interface required)
- Mod simple to apply (4 wires, 4 components changes and a firmware change)
- Mod remains downwards-compatible with the original firmware (except for the loss of DVM function)
- Firmware is Open Source through an Arduino Sketch, it allows experimentation, new features can be easily added, contributions can be shared via Github repository QCX-SSB
- Completely digital and software-based SSB transmit-stage (no additional circuitry needed, except for the audio-in circuit)
- ATMEGA328P signal processing: samples audio-input and reconstruct a SSB-signal by controlling the phase of the SI5351 PLL (through tiny frequency changes over 800kbits/s I2C) and the amplitude of the PA (through PWM of the PA key-shaping circuit).
- Lean and low-cost SSB transceiver design: because of the EER/Polar-transmitter class-E stage it is highly power-efficient (no bulky heatsinks required), and has a simple design (no complex balanced linear power amplifier required)
- An pre-distorion algorithm that cancels out the amplitude errors of non-linearities in the PA voltage regulated PWM supply; a lookup table is used that can be calibrated with an internal PA amplitude measurement
Revision History:
| Rev. | Author | Description |
|---|---|---|
| R1.00 | pe1nnz@amsat.org | Initial release of prototype |
| R1.01 | pe1nnz@amsat.org | Improved audio quality and IMD3 performance and experimental (amplitude) pre-distortion and calibration. Fixed an issue with spurious transmission for RX-TX-RX transitions. NOTE: When upgrading from R1.00 you need to execute installation step 6 (see below). |
Schematic:
RX mod (step 1):
(CW filter) CW
──┐ to IC9A/pin1 ────────o SW C21[]│
┌┴┐ o─────────[]│────to LF amp
│ │ (I/Q phase net) / +[]│
│ │<────────────────────────o /
└┬┘ to R27/pin2 SSB RX 3dB BW
──┘ (200/2200Hz)
Audio-input mod (step 2-5, changes the DVM circuit):
5V┌──────────┐
┌────────────┤AVCC 20 │
│ 1.1V│ │
D4│ R57┌───┤AREF │
10K│ 10K│ │21 │
┌┴┐ ┌┴┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ATMEGA328P│ (Step 7 - only for ISP programming)
│ │ │ │ │ QCX │ ┌─────────┐
└┬┘ └┬┘ │ │ISP-2 │ Arduino │
Paddle/Tip │ || │ │ RESET├───────────┤10 ├────[USB+cable to PC with Arduino
┌──────────+───||───+───┤ADC2 │ISP-3 │ UNO │
│Electret │R58|| │ │25 MOSI├───────────┤11 │
│mic │ 220nF ┌┴┐ │ │ISP-6 │ │
|O ──┴── │ │ │ MISO├───────────┤12 │
│ ──┬── │ │ │ │ISP-4 │ │
│ C42 │ R56└┬┘ │ SCK├───────────┤13 │ <-- runs ArduinoISP
│ 10nF│ 10K │ │22 │ISP-1 │ │
└──────────┴────────┴───┤GND GND├───────────┤GND │
Paddle-jack/Sleeve └──────────┘ └─────────┘ AND... DO NOT FORGET TO CHANGE C31 & C32
Original QCX Schematic (click to zoom): 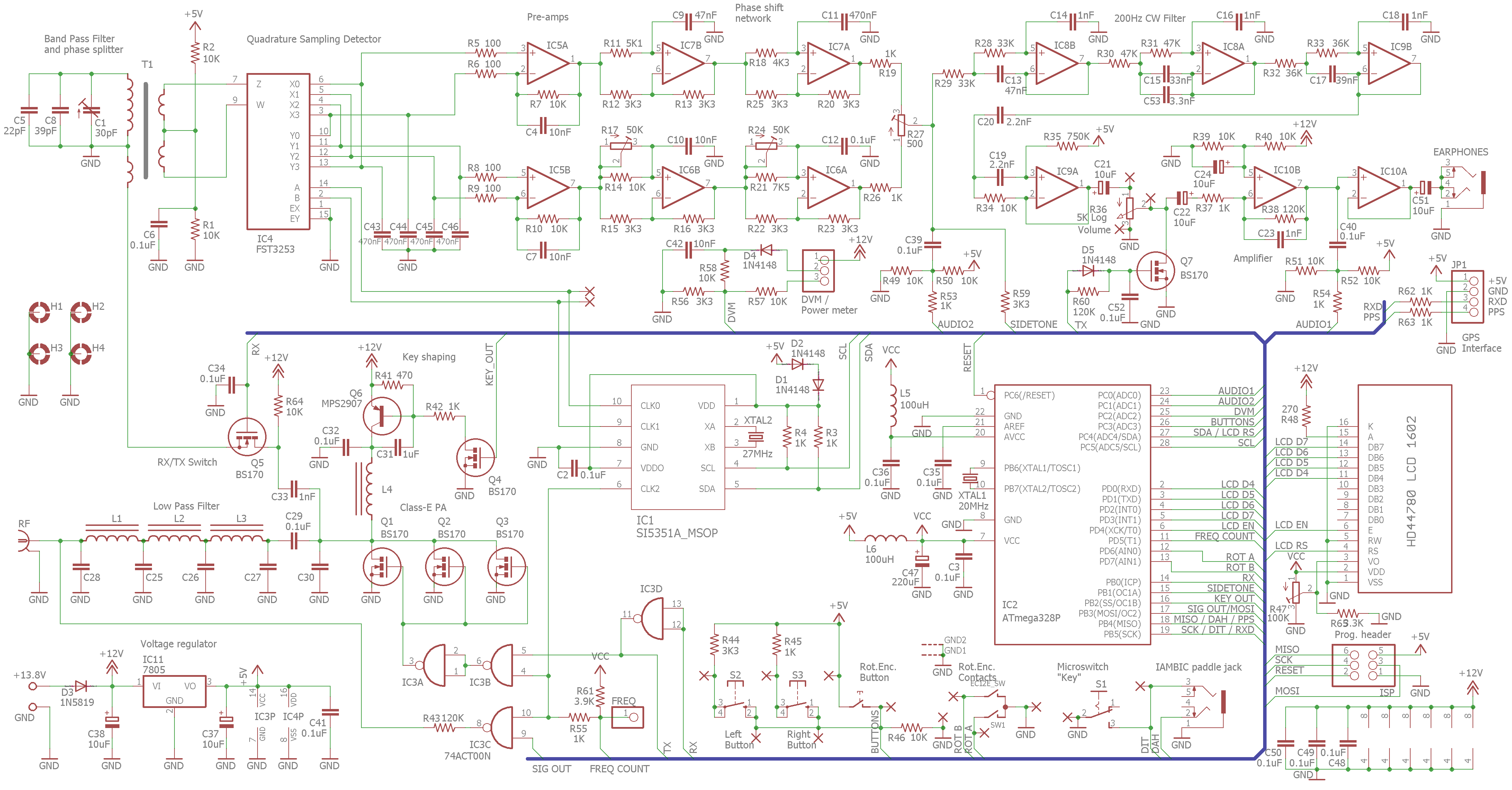
Installation:
You will need to install 4 wires, change 6 components and upload the firmware of this sketch:
- Disconnect +/side of C21 from IC9/pin1 and wire +/side of C21 to R27/pin2, you may1 insert SPDT switch with common to C21 and the throws to IC9/pin1 and R27/pin2 for SSB/CW switching
- Remove D4, insert resistor 10K in D4
- Move R58 (10K) to R56, insert capacitor 220nF in R58
- Move C42 (10nF) to the backside of PCB and place it on the top pads of D4 and C42 that are closest to IC2
- Wire DVM/pin3-R57 to IC2/pin21 (AREF), wire junction D4-C42-R58 to IC2/pin18 (DAH), wire DVM/pin2 to IC2/pin20 (AVCC)
- Remove C31; and replace C32 with 10uF
- Connect an electret microphone (+/-) between Tip (DAH) and Sleeve (GND) of Paddle-jack, PTT-switch between Ring (DIT) and Sleeve (GND) (such as a X1M-mic)
- Upload new firmware via an Arduino UNO board; install and start Arduino environment, connect Arduino Uno to your PC, upload QCX-SSB sketch and place the ATMEGA328P into the QCX. See also 5.
Operation:
Currently, the following functions have been assigned to the buttons:
| Button | Function |
|---|---|
| LEFT single-press | LSB/USB-mode |
| LEFT double-press | reserved |
| LEFT long-press | VOX mode (for full-break-in or digital modes) |
| CENTER single-press | Select frequency step |
| CENTER double-press | Select Band |
| CENTER long-press | Select frequency step (reverse-direction) |
| CENTER turn | Tune frequency |
| RIGHT single-press | Set amplitude drive level on (8=constant carrier on TX) |
| RIGHT double-press | Internal calibration of PA amplitude |
| RIGHT long-press | Sweep over frequency 0..2550Hz and amplitude 0..100% |
| KEY | Transmitter-keyed (PTT) |
Technical Description:
For SSB reception the QCX CW filter is too small, therefore the first modification step 1 is to bypass the CW filter, providing a 3dB wideband passthrough of about 2kHz, this has side-effect that we loose 18dB audio-gain of the CW filter. Another way is to modify the CW-filter 2, but this creates a steep filter-transition band. Insertion of a SPDT switch between the CW filter output, unfiltered output and the audio amplifier input may support CW and SSB mode selection. The phase-network is less efficient for the full SSB bandwidth in attenuating the unwanted side band, but overall a rejection of ~20 dB can still be achieved. LSB/USB mode switching is done by changing the 90 degree phase shift on the CLK1/CLK2 signals of the SI5351 PLL.
For SSB transmission the QCX DVM-circuitry is changed and used as an audio-input circuit (installation steps 2-5). An electret-microphone (with PTT switch) is added to the Paddle jack connecting the DVM-circuitry, whereby the DOT input acts as the PTT and the DASH input acts as the audio-input (installation step 7). The electret microphone is biased with 5V through a 10K resistor. A 10nF blocking capacitor prevents RF leakage into the circuit. The audio is fed into ADC2 input of the ATMEGA328P microprocessor through a 220nF decoupling capacitor. The ADC2 input is biased at 0.55V via a divider network of 10K to a 1.1V analog reference voltage, with 10-bits ADC resolution this means the microphone-input sensitivity is about 1mV (1.1V/1024) which is just sufficient to process unamplified speech.
A new QCX-SSB firmware is uploaded to the ATMEGA328P (installation step 8), and facilitates a digital SSB generation technique in a completely software-based manner. A DSP algorithm samples the ADC2 audio-input at a rate of 4400 samples/s, performs a Hilbert transformation and determines the phase and amplitude of the complex-signal; the phase-changes are restricted4 and transformed into either positive (for USB) or negative (for LSB) phase changes which in turn transformed into temporary frequency changes which are sent 4400 times per second over 800kbit/s I2C towards the SI5351 PLL. This result in phase changes on the SSB carrier signal and delivers a SSB-signal with a bandwidth of 2200 Hz whereby spurious in the opposite side-band components is attenuated.
The amplitude of the complex-signal controls the supply-voltage of the PA, and thus the envelope of the SSB-signal. The key-shaping circuit is controlled with a 32kHz PWM signal, which can control the PA voltage from 0 to about 12V in 256 steps, providing a dynamic range of (log2(256) * 6 =) 48dB in the SSB signal. C31 is removed (installation step 6) to ensure that Q6 is operating as a digital switch, this improves the efficiency, thermal stability, linearity, dynamic range and response-time. Though the amplitude information is not mandatory to make a SSB signal intelligable, adding amplitude information improves quality. The complex-amplitude is also used in VOX-mode to determine when RX and TX transitions are supposed to be made.
The IMD performance is related dependent on the quality of the system: the linearity (accuracy) of the amplitude and phase response and the precision (dynamic range) of these quantities. Especially the DSP bit-width, the precision used in the DSP algorithms, the PWM and key-shaping circuit that supplies the PA and the PA phase response are critical. The following has been done to improve the quality (since v1.01): A. use a more accurate I/Q amplitude estimation algorithm; B. pre-distort, cancel out PA induced amplitude and (amplitude-dependent) phase-errors, the ssb generation algorithm applies a amplitude correction through a (amplitude) lookup in a predefined table before modulating.
Notes:
- on a new kit components IC8, IC9, R28-R35, C13-C20, C53 may be omitted if the CW filter is bypassed permanently
- optionally (not recommended) a steep 2 kHz SSB filter with gain can be realized by modification of Sallen-Key CW filter: replace C13, C15, C17 with 1nF capacitor and remove C53
- to support si5351 multi-band operation, the RX BPF can be omitted (C1, C5, C8, secondary 3 of T1), and a switchable LPF-bank/matching-network may be placed instead of the existing LPF C25-C28, L1-L3 and matching network C29, C30, L4. The Arduino sketch may be extended to make I2C controllable filter-bank. When using external filters the on-board LPF may be bypassed with a wire.
- The occupied SSB bandwidth can be further reduced by restricting the maximum phase change (set MAX_DP to 180). The sensitivity of the VOX switching can be set with parameter VOX_THRESHOLD. Audio-input can be attenuated by increasing parameter MIC_ATTEN (6dB per step).
- If the ATMEGA328P chip cannot be exchanged you may proceed with ISP programming the QCX via Uno and overwrite the existing firmware: to do so, upload the ArduinoISP sketch to Uno, connect Arduino Uno to QCX via ISP jumper, power on QCX, in Arduino select "Tools > Programmer > Arduino as ISP", select "Tools > Board > Arduino/Genuino Uno", and upload QCX-SSB Sketch to QCX by selecting "Sketch > Upload Using Programmer". Once upload succeeds the LCD should display "QCX-SSB".
Credits
QCX (QRP Labs CW Xcvr) is a kit designed by Hans Summers (G0UPL), a high performance, image rejecting DC transceiver; basically a simplified implementation of the NorCal 2030 by Dan Tayloe (N7VE) designed in 2004 combined with a Hi-Per-Mite Active Audio CW Filter by David Cripe (NMØS), Low Pass Filters from Ed (W3NQN) 1983 Articles, a key-shaping circuit by Donald Huff (W6JL), a BS170 switched CMOS driven MOSFET PA stage as used by Steven Weber (KD1JV) inspired by Frank Cathell (W7YAZ) in 1988, and combined with popular components such as a Silicon Labs SI5351 Clock Generator, ATMEGA328P microprocessor and a HD44700 LCD display. The QCX-SSB modification and its Arduino QCX-SSB Sketch is designed by Guido (PE1NNZ); the software-based SSB transmit stage is a derivate of earlier experiments with a digital SSB generation technique on a Raspberry Pi in 2013 and is basically a kind of EER implemented in software.
