|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| cli | ||
| example | ||
| lib | ||
| scripts | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| MIGRATING.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
| index.html | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| preview.png | ||
README.md
StatiCrypt
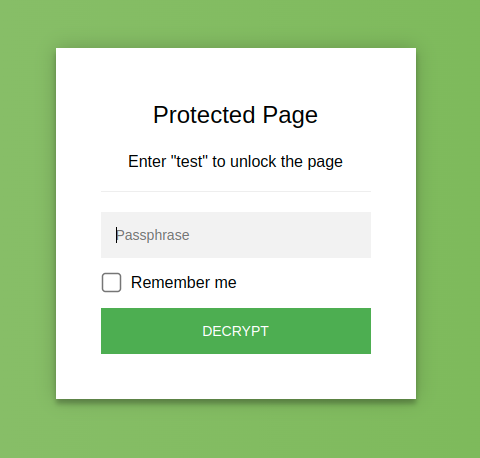
StatiCrypt uses AES-256 and WebCrypto to encrypt your HTML file with your long password and return a static page including a password prompt and the javascript decryption logic that you can safely upload anywhere (see what the page looks like).
This means you can password protect the content of your public static HTML file, without any back-end - serving it over Netlify, GitHub pages, etc. (see the detail of how it works).
You can encrypt a file online in your browser (client side) at https://robinmoisson.github.io/staticrypt, or use the CLI to do it in your build process.
CLI
Migration: v3 brings many improvements, a clearer CLI and simpler password_template over v2. See the migration guide from v2 to v3. v3 uses WebCrypto which is only available in HTTPS or localhost contexts, so if you need to use it in HTTP you'll need to use v2.
Installation
Staticrypt is available through npm as a CLI, install with
npm install staticrypt
You can then run it with npx staticrypt .... You can also install globally with npm install -g staticrypt and then just call staticrypt ....
Examples
These examples will create a
.staticrypt.jsonfile in the current directory, see the FAQ as to why. You can prevent it by setting the--configflag to "false".
Encrypt a file: encrypt test.html and create a encrypted/test.html file (use -d my_directory to change the output directory):
staticrypt test.html -p MY_LONG_PASSWORD
Encrypt a file with the password in an environment variable: set your long password in the STATICRYPT_PASSWORD environment variable (.env files are supported):
# the password is in the STATICRYPT_PASSWORD env variable
staticrypt test.html
Encrypt a file and get a shareable link containing the hashed password - you can include your file URL or leave blank:
# you can also pass '--share' without specifying the URL to get the `#staticrypt_pwd=...`
staticrypt test.html -p MY_LONG_PASSWORD --share https://example.com/test_encrypted.html
# => https://example.com/test_encrypted.html#staticrypt_pwd=5bfbf1343c7257cd7be23ecd74bb37fa2c76d041042654f358b6255baeab898f
Encrypt all html files from a directory and put them in a encrypted/ directory ({} will be replaced with each file name by the find command):
find . -type f -name "*.html" -exec staticrypt {} -p MY_LONG_PASSWORD \;
CLI Reference
The password argument is optional if STATICRYPT_PASSWORD is set in the environment or .env file.
Usage: staticrypt <filename> [options]
Options:
--help Show help [boolean]
--version Show version number [boolean]
-c, --config Path to the config file. Set to "false" to
disable. [string] [default: ".staticrypt.json"]
-d, --directory Name of the directory where the encrypted files
will be saved. [string] [default: "encrypted/"]
-p, --password The password to encrypt your file with. Leave
empty to be prompted for it. If
STATICRYPT_PASSWORD is set in the env, we'll use
that instead. [string] [default: null]
--remember Expiration in days of the "Remember me" checkbox
that will save the (salted + hashed) password in
localStorage when entered by the user. Set to
"false" to hide the box. Default: "0", no
expiration. [number] [default: 0]
-s, --salt Set the salt manually. It should be set if you
want to use "Remember me" through multiple pages.
It needs to be a 32-character-long hexadecimal
string.
Include the empty flag to generate a random salt
you can use: "statycrypt -s". [string]
--share Get a link containing your hashed password that
will auto-decrypt the page. Pass your URL as a
value to append "#staticrypt_pwd=<hashed_pwd>",
or leave empty to display the hash to append.
[string]
--short Hide the "short password" warning.
[boolean] [default: false]
-t, --template Path to custom HTML template with password
prompt.
[string] [default: "/code/staticrypt/lib/password_template.html"]
--template-button Label to use for the decrypt button. Default:
"DECRYPT". [string] [default: "DECRYPT"]
--template-instructions Special instructions to display to the user.
[string] [default: ""]
--template-error Error message to display on entering wrong
password. [string] [default: "Bad password!"]
--template-placeholder Placeholder to use for the password input.
[string] [default: "Password"]
--template-remember Label to use for the "Remember me" checkbox.
[string] [default: "Remember me"]
--template-title Title for the output HTML page.
[string] [default: "Protected Page"]
HOW STATICRYPT WORKS
So, how can you password protect html without a back-end?
StatiCrypt uses WebCrypto to generate a static, password protected page that can be decrypted in-browser. You can then just send or upload the generated page to a place serving static content (github pages, for example) and you're done: the page will prompt users for a password, and the javascript will decrypt and load your HTML, all done in the browser.
So it basically encrypts your page and puts everything in a user-friendly way to enter the password in the new file.
FAQ
Is it secure?
Simple answer: your file content has been encrypted with AES-256, a popular and strong encryption algorithm. You can now upload it to any public place and no one will be able to read it without the password. So if you used a long, strong password, then yes it should be pretty secure.
That being said, actual security always depends on a number of factors and on the threat model you want to protect against. Because your full encrypted file is accessible client side, brute-force/dictionary attacks would be easy to do at a really fast pace: use a long, unusual password. We recommend 16+ alphanum characters, Bitwarden is a great open-source password manager if you don't have one already.
On the technical aspects: we use AES in CBC mode (see a discussion on why this mode is appropriate for StatiCrypt in #19) and 600k PBKDF2-SHA256 iterations (which is the recommended number by OWASP - read a detailed report on why this number and the security model of StatiCrypt in #159).
Also, disclaimer: I am not a cryptographer - I try my best to get the implementation right, listen to feedback and be transparent but please adjust accordingly depending on your threat model. If you are an at-risk activist or have sensitive crypto assets to protect, you might want to use something else.
Can I customize the password prompt?
Yes! Just copy lib/password_template.html, modify it to suit your style and point to your template file with the -t path/to/my/file.html flag.
Be careful to not break the encrypting javascript part, the variables replaced by StatiCrypt are in this format: /*[|variable|]*/0. Don't leave out the 0 at the end, this weird syntax is to avoid conflict with other templating engines while still being read as valid JS to parsers so we can use auto-formatting on the template files.
Can I remove the "Remember me" checkbox?
If you don't want the checkbox to be included, you can set the --remember false flag to disable it.
Why doesn't StatiCrypt work in HTTP?
From version 3.x StatiCrypt only uses the browser WebCrypto API, which makes it more secure but is only available in HTTPS or on localhost. If you need to use it in HTTP, you can use version 2.x which offers the CryptoJS engine as an option, and will work everywhere.
Why does StatiCrypt create a config file?
The "Remember me" feature stores the user password hashed and salted in the browser's localStorage, so it needs the salt to be the same each time you encrypt otherwise the user would be logged out when you encrypt the page again. The config file is a way to store the salt in between runs, so you don't have to remember it and pass it manually.
When deciding what salt to use, StatiCrypt will first look for a --salt flag, then try to get the salt from the config file, and if it still doesn't find a salt it will generate a random one. It then saves the salt in the config file.
If you don't want StatiCrypt to create or use the config file, you can set --config false to disable it.
The salt isn't secret, so you don't need to worry about hiding the config file.
How does the "Remember me" checkbox work?
The CLI will add a "Remember me" checkbox on the password prompt by default (--remember false to disable). If the user checks it, the (salted + hashed) password will be stored in their browser's localStorage and the page will attempt to auto-decrypt when they come back.
If no value is provided the stored password doesn't expire, you can also give it a value in days for how long should the store value be kept with --remember NUMBER_OF_DAYS. If the user reconnects to the page after the expiration date the stored value will be cleared.
"Logging out"
You can clear StatiCrypt values in localStorage (effectively "logging out") at any time by appending staticrypt_logout to the URL fragment (https://mysite.com#staticrypt_logout).
Encrypting multiple pages
This allows encrypting multiple page on a single domain with the same password: if you check "Remember me", you'll have to enter your password once then all the pages on that domain will automatically decrypt their content. Because the hashed value is stored in the browser's localStorage, this will only work if all the pages are on the same domain name.
Is the "Remember me" checkbox secure?
In case the value stored in the browser becomes compromised an attacker can decrypt the page, but because it's stored salted and hashed this should still protect against password reuse attacks if you've used the password on other websites (of course, please use a long, unique password nonetheless).
Contributing
🙏 Thank you!
- @AaronCoplan for bringing the CLI to life
- @epicfaace & @thomasmarr for sparking the caching of the password in localStorage (allowing the "Remember me" checkbox)
- @hurrymaplelad for refactoring a lot of the code and making the project much more pleasant to work with
- @hurrymaplelad and @tarpdalton for their work in bringing WebCrypto to StatiCrypt
Opening PRs and issues
You're free to open PRs if you're ok with having no response for a (possibly very) long time and me possibly ending up getting inspiration from your proposal but merging something different myself (I'll try to credit you though). Apologies in advance for the delay, and thank you!
It's fine to open issues with suggestions and bug reports.
If you find a serious security bug please open an issue, I'll try to fix it relatively quickly.
Security
You can find the security policy and secure contact details in SECURITY.md. If you have general ideas or feedback around the implementation or StatiCrypt security model they are very welcome, if it's not extra sensitive feel free to open an issue. A couple of place where security was discussed previously are #19 and #159.
Guidelines to contributing
Source map
cli/- The command-line interface published to NPM.example/- Example encrypted files, used as an example in the public website and for manual testing.lib/- Files shared across www and cli.scripts/- Convenient scripts for building the project.index.html- The root of the in-browser encryption site hosted at https://robinmoisson.github.io/staticrypt. Kept in the root of the repo for easy deploys to GitHub Pages.
Build
When editing StatiCrypt logic, we want to reflect the changes in the browser version, the CLI and the example files. To do so, run:
npm install
npm run build
Test
The testing is done manually for now - you can run build, then open example/encrypted/example.html and check everything works correctly. There is an open issue to automate this in #136, feel free to contribute to setting up a test framework if you'd like!
Community and alternatives
Here are some other projects and community resources you might find interesting (this is included as an informative section, I haven't personally vetted any of those).
Alternatives to StatiCrypt
MaxLaumeister/PageCrypt is a project with similar features in a different style (I think it was created before StatiCrypt).
Based on StatiCrypt
Template to host an encrypted single page website with Github Pages: a-nau/password-protected-website-template is a demonstration of how to build a protected page on Github Pages, integrating with Github Actions