|
…
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| modssb.pro | ||
| readme.md | ||
| ssbmod.cpp | ||
| ssbmod.h | ||
| ssbmodgui.cpp | ||
| ssbmodgui.h | ||
| ssbmodgui.ui | ||
| ssbmodplugin.cpp | ||
| ssbmodplugin.h | ||
readme.md
SSB modulator plugin
Introduction
This plugin can be used to generate a single sideband or double sidebands modulated signal.
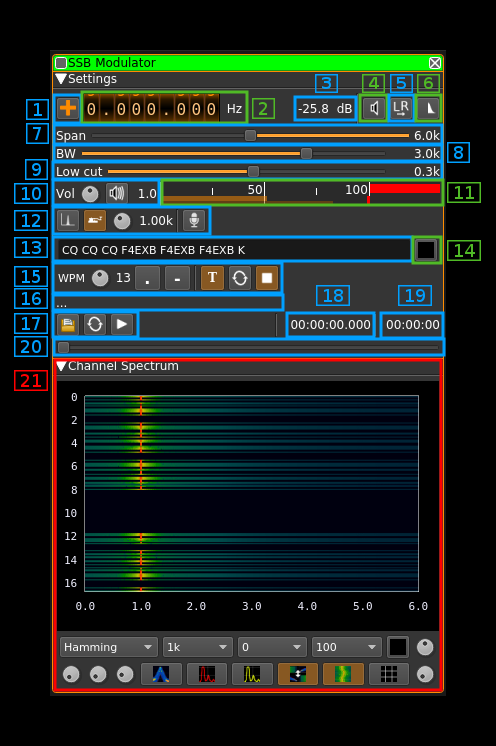
Interface
1: Frequency shift from center frequency of reception direction
The "+/-" button on the left side of the dial toggles between positive and negative shift.
2: Frequency shift from center frequency of reception value
Use the wheels to adjust the frequency shift in Hz from the center frequency of reception. Left click on a digit sets the cursor position at this digit. Right click on a digit sets all digits on the right to zero. This effectively floors value at the digit position.
3: Channel power
Average total power in dB relative to a +/- 1.0 amplitude signal generated in the pass band.
4: Binaural mode
Use this button to toggle between monaural and binaural mode. Monaural is classical single sideband or double sidebands modulation. In binaural mode I and Q samples are taken from the left and right stereo channels (or reversed).
When in monaural mode the icon shows a single loudspeaker and when in binaural mode it shows a pair of loudspeakers.
5: Reverse left and right channels in binaural mode
Effective only in binaural mode: reverses left and right audio channels so that the left is connected to Q and the right to the I complex signal channel.
6: SSB/DSB
Selects between SSB and DSB operation. When in SSB mode the icon shows a single sideband spectrum (USB side). When in DSB mode the icon shows a double sideband spectrum.
7: Spectrum display frequency span
The transmitted signal in the sideband (SSB) or sidebands (DSB) is further decimated by a power of two before being applied to the channel spectrum display. Thus the frequency span of the spectrum display is the audio sample rate (48 kHz) divided by the decimation factor.
8: Signal bandwidth
The modulating signal is bandpass filtered (SSB) or lowpass filtered (DSB) before being multiplied by the local oscillator NCO. This is the upper limit of the filter in absolute value.
When this limit is positive the signal is transmitted in the upper sideband (USB). When this limit is negative the signal is transmitted in the lower sideband (LSB).
9: Filter low frequency cutoff
In SSB mode this is the lower limit in absolute value of the modulating signal bandpass filter
10: Volume
This is the volume of the audio signal from 0.0 (mute) to 2.0 (maximum). It can be varied continuously in 0.1 steps using the dial button. The Loudspeaker button is the audio mute toggle.
11: Level meter in %
- top bar (beige): average value
- bottom bar (brown): instantaneous peak value
- tip vertical bar (bright red): peak hold value
You should aim at keepimg the peak value below 100% using the volume control
12: Input source control
12.1: Tone input select
Switches to the tone input. You must switch it off to make other inputs available.
12.2: Morse keyer input select
Switches to the Morse keyer input. You must switch it off to make other inputs available.
12.3: Tone frequency (kHz)
Adjusts the tone frequency from 0.1 to 2.5 kHz in 0.01 kHz steps
12.4: Audio input select
Switches to the audio input. You must switch it off to make other inputs available.
13: CW (Morse) text
Enter the text to be keyed when Morse input is active and in text mode
14: Clear CW text
Clears the CW (Morse) text
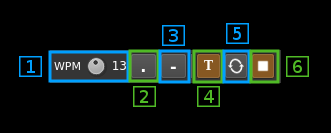
15: Morse keyer controls
15.1: CW keying speed
Sets the CW speed in Words Per Minute (WPM). This is based on the word "PARIS" sent 5 times. For 5 WPM the dot length is 240 ms. In other terms the dot length is calculated as 1.2 / WPM seconds. The dot length is used as the base to compute other timings:
- Element (dot or dash) silence separator: 1 dot length
- Dash: 3 dot lengths
- Character silence separator: 3 dot lengths
- Word silence separator: 7 dot lengths
15.2: Dots keying
Switch this button to send dots continuously
15.3: Dashes keying
Switch this button to send dashes continuously
15.4: Text keying
Switch this button to send the text typed into the text box (13)
15.5: Text auto repeat
Switch this button to auto repeat the text keying
15.6: Text play/stop
Use this button to stop sending text. When resuming keying restarts at the start of text
16: Audio file path
The path to the selected audio file to be played or dots if unselected
17: Audio file play controls
17.1: Audio file select
Opens a file dialog to select the audio file to be played. It must be mono 48 kHz 16LE raw format.
17.2: Audio file loop
Audio replay file at the end
17.3: Play/pause file play
Toggle play/pause file play. When paused the slider below (20) can be used to randomly set the position in the file when re-starting.
18: Play file current position
This is the current audio file play position in time units relative to the start
19: Play file length
This is the audio file play length in time units
20: Play file position slider
This slider can be used to randomly set the currennt position in the file when file play is in pause state (button 17.3)
21: Channel spectrum display
This is the channel spectrum display. Controls at the bottom of the panel are the same as with the central spectrum display.