Add support for different map types (street/satellite) and different map providers. Support finding real world addresses on the map. Add Maidenhead locator converter. Add Beacons. Allow data sources to be selected by a user. Add context menu to allow setting an object as a target, setting center frequency and adjusting display order. |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| gs232controller.cpp | ||
| gs232controller.h | ||
| gs232controllergui.cpp | ||
| gs232controllergui.h | ||
| gs232controllergui.ui | ||
| gs232controllerplugin.cpp | ||
| gs232controllerplugin.h | ||
| gs232controllerreport.h | ||
| gs232controllersettings.cpp | ||
| gs232controllersettings.h | ||
| gs232controllerwebapiadapter.cpp | ||
| gs232controllerwebapiadapter.h | ||
| gs232controllerworker.cpp | ||
| gs232controllerworker.h | ||
| readme.md | ||
readme.md
GS-232 Rotator Controller Feature Plugin
Introduction
The GS-232 Rotator Controller feature plugin allows SDRangel to send commands to GS-232 rotators. This allows SDRangel to point antennas mounted on a rotator to a specified azimuth and elevation.
Azimuth and elevation can be set manually by a user in the GUI, via the REST API, or via another plugin, such as the Map Feature, the ADS-B Demodulator, or the Star Tracker.
Interface
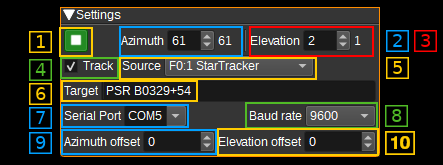
1: Start/Stop plugin
This button starts or stops the plugin. When the plugin is stopped, azimuth and elevation commands will not be sent to the GS-232 rotator.
2: Azimuth
Specifies the target azimuth (angle in degrees, clockwise from North) to point the antenna towards. Valid values range from 0 to 450 degrees. The value to the right of the target azimuth, is the current azimuth read from the GS-232 rotator.
3: Elevation
Specifies the target elevation (angle in degrees) to point the antenna towards. Valid values range from 0 to 180 degrees, where 0 and 180 point towards the horizon and 90 degrees to zenith. The value to the right of the target elevation, is the current elevation read from the GS-232 rotator.
4: Track
When checked, the target azimuth and elevation will be controlled by the Channel or Feature Source (5). For example, this allows an aircraft to be tracked, by setting the Source to the ADS-B Demodulator plugin, or the Moon to be tracked by settng Source to the Star Tracker plugin.
5: Source
Specify the SDRangel Channel or Feature that that will control the target aziumth and elevation values, when Track (4) is checked.
6: Target
When tracking is enabled, this field will display a name for the target being tracked, as indicated by the selected Source plugin (5). For example, the ADS-B plugin will display the flight number of the target aircraft. The Star Tracker plugin will display Sun, Moon or Star.
7: Serial Port
Specifies the serial port (E.g. COM3 on Windows or /dev/ttyS0 on Linux) that will be used to send commands to the GS-232 rotator.
8: Baud rate
Specifies the baud rate that will be used to send commands to the GS-232 rotator. Typically this is 9600.
9: Azimuth Offset
The azimuth offset specifies an angle in degrees that is added to the target azimuth before sending to the controller. This allows for a misalignment of the rotator to be corrected.
10: Elevation Offset
The elevation offset specifies an angle in degrees that is added to the target elevation before sending to the controller. This allows for a misalignment of the rotator to be corrected.
API
Full details of the API can be found in the Swagger documentation. Here is a quick example of how to set the azimuth and elevation from the command line:
curl -X PATCH "http://127.0.0.1:8091/sdrangel/featureset/0/feature/0/settings" -d '{"featureType": "GS232Controller", "GS232ControllerSettings": { "azimuth": 180, "elevation": 45 }}'
To start sending commands to the rotator:
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:8091/sdrangel/featureset/0/feature/0/run"