|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| adc | ||
| driver | ||
| easygpio | ||
| firmware | ||
| httpclient | ||
| include | ||
| ntp | ||
| pwm | ||
| scripts | ||
| uMQTTBroker@724bf8f830 | ||
| user | ||
| user_basic | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| Makefile.orig | ||
| README.md | ||
| SCRIPTING.md | ||
| SublimeAStyleFormatter.sublime-settings | ||
README.md
esp_uMQTT_broker
An MQTT Broker/Client with scripting support on the ESP8266
This program enables the ESP8266 to become the central node in a small distributed IoT system. It implements an MQTT Broker and a simple scripted rule engine with event/action statements that links together the MQTT sensors and actors. It can act as STA, as AP, or as both and it can connect to another MQTT broker (i.e. in the cloud). Here it can also be bridge that forwards and rewrites topics in both directions. Also it can parse JSON structures, send basic HTTP GET requests and do basic I/O: i.e. read and write to local GPIO pins, react on timers and GPIO interrupts, drive GPIO pins with PWM, and read the ADC.
Find a video that explains the ideas and the architecture of the project at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0K9q4IuB_oA
You can use the pure broker functionality (not the CLI and the scripting) in any ESP Arduino project as a libary by going to https://github.com/martin-ger/uMQTTBroker . Just clone (or download the zip-file and extract it) into the libraries directory of your Arduino ESP8266 installation.
Usage
In the user directory there is the main program that serves as a stand-alone MQTT broker, client and bridge. The program starts with the following default configuration:
- ap_ssid: MyAP, ap_password: none, ap_on: 1, ap_open: 1
- network: 192.168.4.0/24
This means it starts an open AP with ap_ssid MyAP. This default can be changed in the file user_config.h. The default can be overwritten and persistenly saved to flash by using a console interface. This console is available either via the serial port at 115200 baud or via tcp port 7777 (e.g. "telnet 192.168.4.1 7777" from a connected STA). It does not yet try to automatically re-connect to an uplink AP (as it does not know a valid ssid or password).
Use the following commands for an initial setup:
- set ssid your_home_router's_SSID
- set password your_home_router's_password
- set ap_ssid ESP's_ssid
- set ap_password ESP's_password
- show (to check the parameters)
- save
- reset
After reboot it will try to automatically connect to your home router and itself as AP is ready for stations to connect.
The console understands the following commands:
General commands:
- help: prints a short help message
- show [config|stats]: prints the current config or some status information and statistics
- save: saves the current config parameters to flash
- lock [password]: saves and locks the current config, changes are not allowed. Password can be left open if already set before
- unlock password: unlocks the config, requires password from the lock command
- reset [factory]: resets the esp, 'factory' optionally resets WiFi params to default values (works on a locked device only from serial console)
- set speed [80|160]: sets the CPU clock frequency (default 80 Mhz)
- set config_port portno: sets the port number of the console login (default is 7777, 0 disables remote console config)
- set config_access [0|1|2|3]: controls the networks that allow config access (0: no access, 1: only internal, 2: only external, 3: both (default))
- set bitrate [bps]: sets the serial bitrate (default 115200 bps)
- set system_output [0|1|2]: configures systems handling of the serial port (0: none/script, 1: cli commands/responses, 2: cli and info/warnings (default)). Mode 0 means, that any serial input is forwarded to the scripting engine if enabled
- quit: terminates a remote session
WiFi and network related commands:
- set [ssid|password] value: changes the settings for the uplink AP (WiFi config of your home-rou- set [ap_ssid|ap_password] value: changes the settings for the soft-AP of the ESP (for your stations)ter)
- set ap_on [0|1]: selects, whether the soft-AP is disabled (ap_on=0) or enabled (ap_on=1, default)
- set ap_open [0|1]: selects, whether the soft-AP uses WPA2 security (ap_open=0, automatic, if an ap_password is set) or open (ap_open=1)
- set auto_connect [0|1]: selects, whether the WiFi client should automatically retry to connect to the uplink AP (default: on=1)
- set network ip-addr: sets the IP address of the SoftAP's network, network is always /24, esp_uMQTT_broker is always x.x.x.1
- set dns dns-addr: sets a static DNS address
- set dns dhcp: configures use of the dynamic DNS address from DHCP, default
- set ip ip-addr: sets a static IP address for the ESP in the uplink network
- set ip dhcp: configures dynamic IP address for the ESP in the uplink network, default
- set netmask netmask: sets a static netmask for the uplink network
- set gw gw-addr: sets a static gateway address in the uplink network
- set mdns_mode [0|1|2]: selects, which interface should be announced via mDNS (0: none (default), 1: STA, 2: SoftAP)
- scan: does a scan for APs
While the user interface looks similar to my esp_wifi_repeater at https://github.com/martin-ger/esp_wifi_repeater this does NO NAT routing. AP and STA network are stricly separated and there is no routing in between. The only possible connection via both networks is the uMQTT broker that listens on both interfaces.
MQTT broker related command:
- show [mqtt]: prints the current config or status information of the MQTT broker
- set broker_user unsername: sets the username for authentication of MQTT clients ("none" if no auth, default)
- set broker_password password: sets the password for authentication of MQTT clients ("none" if empty, default)
- set broker_access mode: controls the networks that allow MQTT broker access (0: no access, 1: only internal, 2: only external, 3: both (default))
- set broker_subscriptions max: sets the max number of subscription the broker can store (default: 30)
- set broker_retained_messages max: sets the max number of retained messages the broker can store (default: 30)
- set broker_clients clients_max: sets the max number of concurrent client connections (default: 0 = mem is the only limit)
- save_retained: saves the current state of all retained topics (max. 4096 Bytes in sum) to flash, so they will persist a reboot
- delete_retained: deletes the state of all retained topics in RAM and flash
- set broker_autoretain [0|1]: selects, whether the broker should do a "save_retained" automatically each time it receives a new retained message (default off). With this option on the broker can be resetted at any time without loosing state. However, this is slow and too many writes may damage flash mem.
MQTT client/bridging functionality
The broker comes with a "local" and a "remote" client, which means, the broker itself can publish and subscribe topics. The "local" client is a client to the own broker (without the need of an additional TCP connection).
By default the "remote" MQTT client is disabled. It can be enabled by setting the config parameter "mqtt_host" to a hostname different from "none". To configure the "remote" MQTT client you can set the following parameters:
- set mqtt_host IP_or_hostname: IP or hostname of the MQTT broker ("none" disables the MQTT client)
- set mqtt_user username: Username for authentication ("none" if no authentication is required at the broker)
- set mqtt_user password: Password for authentication
- set mqtt_ssl [0|1]: Use SSL for connection to the remote broker (default: 0 = off)
- set mqtt_id clientId: Id of the client at the broker (default: "ESPRouter_xxxxxx" derived from the MAC address)
- publish [local|remote] topic data [retained]: this publishes a topic (mainly for testing)
The remote MQTT server can be accessed via SSL, e.g. a secure test connection to test.mosquitto.org can be configured as following:
CMD>set mqtt_host test.mosquitto.org
CMD>set mqtt_port 8883
CMD>set mqtt_ssl 1
CMD>save
CMD>reset
Certificate checks are not yet implemented.
Scripting
The esp_uMQTT_broker comes with a build-in scripting engine. A script enables the ESP not just to act as a passive broker but to react on events (publications and timing events), to send out its own items and handle local I/O. Details on syntax and semantics of the scripting language can be found here: https://github.com/martin-ger/esp_mqtt/blob/master/SCRIPTING.md . Examples of scripts are in the "scripts" directory.
The script specific CLI commands are:
- script [portno|delete]: opens port for upload of scripts or deletes the current script
- show script [line_no]: dumps the currently active script starting with the given line (dumpy only about 1 KB, repeat command for more lines)
- set @[num] value: sets the flash variable "num" (for use in scripts) to the given inital value (must be shorter than 63 chars)
- set pwm_period period: sets the PWM period in terms of 200ns slots (default: 5000, = 0.1ms ^= 1KHz)
- show vars: dumps all variables of the current program incl. the persistent flash variables
- set script_logging [0|1]: switches logging of script execution on or off (not permanently stored in the configuration)
Scripts with size up to 4KB are uploaded to the esp_uMQTT_broker using a network interface.
There are two options to upload a script:
Script Pull (http)
For this, you first have to make the scripts available via a web server. A quite simple way to do that is to start a minimal web server in the "scripts" directory, i.g. on Linux you can start a server on port 8080 on the delevopment machine with:
$ cd scripts
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8080
Another way of course is to upload the script to a real server somewhere on the web.
Then start the download with the command "script " on the concole of the ESP, e.g. like this with the correct hostname and port:
CMD>script http://myserver:8080/scripts/script.new
HTTP request to myserver:8080/scripts/script.new started
HTTP script download completed (330 Bytes)
Syntax okay
CMD>
You can also download over the internet, e.g. directly from github:
CMD>script https://raw.githubusercontent.com/martin-ger/esp_mqtt/master/scripts/script.pwm
HTTP request to https://raw.githubusercontent.com/martin-ger/esp_mqtt/master/scripts/script.pwm started
HTTP script download completed (749 Bytes)
Syntax okay
CMD>
The ESP tries to download the script from the given URL and prints upon success or failure a report on the console.
Script Push (netcat)
Another option is to upload the script as plain TCP stream. Start the upload with "script " on the console of the ESP, e.g.:
CMD>script 2000
Waiting for script upload on port 2000
CMD>
Now the ESP listens on the given port for an incoming connection and stores anything it receives as new script. Upload a file using netcat, e.g.:
$ netcat 192.168.178.29 2000 < user/demo_script2
The ESP will store the file and immediatly checks the syntax of the script:
CMD>script 2000
Waiting for script upload on port 2000
Script upload completed (451 Bytes)
Syntax okay
CMD>
You can examine the currently loaded script using the "show script" command. It only displays about 1KB of a script. If you need to see more, use "show script <line_no>" with a higher starting line. Newly loaded scripts are stored persistently in flash and will be executed after next reset if they contain no syntax errors. "script delete" stops script execution and deleted a script from flash.
NTP Support
NTP time is supported and timestamps are only available if the sync with an NTP server is done. By default the NTP client is enabled and set to "1.pool.ntp.org". It can be changed by setting the config parameter "ntp_server" to a hostname or an IP address. An ntp_server of "none" will disable the NTP client. Also you can set the "ntp_timezone" to an offset from GMT in hours. The system time will be synced with the NTP server every "ntp_interval" seconds. Here it uses NOT the full NTP calculation and clock drift compensation. Instead it will just set the local time to the latest received time.
After NTP sync has been completed successfully once, the local time will be published every second under the topic "$SYS/broker/time" in the format "hh:mm:ss". You can also query the NTP time using the "time" command from the commandline.
- set ntp_server IP_or_hostname: sets the name or IP of an NTP server (default "1.pool.ntp.org", "none" disables NTP)
- set ntp_interval interval: sets the NTP sync interval in seconds (default 300)
- set ntp_timezone tz: sets the timezone in hours offset (default 0)
- time: prints the current time as ddd hh:mm:ss
mDNS
mDNS is supported and depending on "mdns_mode" the broker responds on the name "mqtt.local" with one of its two addresses:
- set mdns_mode [0|1|2]: selects, which interface address should be announced via mDNS (0=none (default), 1 = STA, 2 = SoftAP)
Building and Flashing
The code can be used in any project that is compiled using the NONOS_SDK or the esp-open-sdk. Also the complete broker in the user directory can be build using the standard SDKs after adapting the variables in the Makefile.
Download the repository using
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/martin-ger/esp_mqtt.git
Configure the build options in "user_config.h", then build the esp_uMQTT_broker firmware with "make". "make flash" flashes it onto an esp8266.
If you want to use the precompiled binaries from the firmware directory you can flash them directly on an ESP8266, e.g. with
$ esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 write_flash -fs 32m 0x00000 firmware/0x00000.bin 0x10000 firmware/0x10000.bin
On Windows you can flash it using the "ESP8266 Download Tool" available at https://espressif.com/en/support/download/other-tools. Download the two files 0x00000.bin and 0x10000.bin from the firmware directory. For a generic ESP12, a NodeMCU or a Wemos D1 use the following settings (for an ESP-01 change FLASH SIZE to "8Mbit"):
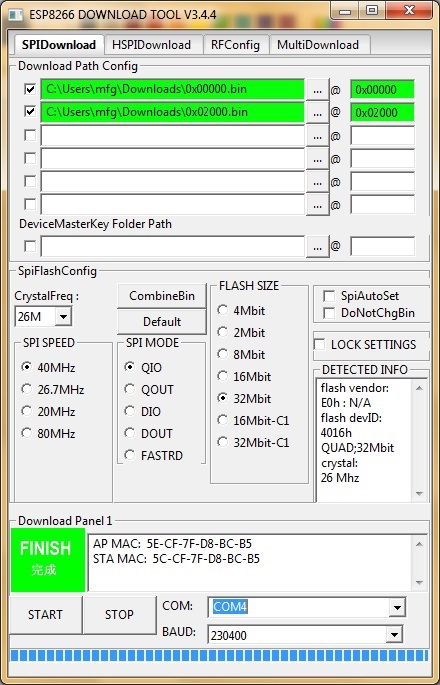
If "QIO" mode fails on your device, try "DIO" instead. Also have a look at the "Detected Info" to check size and mode of the flash chip. If your downloaded firmware still doesn't start properly, please check with the enclosed checksums whether the binary files are possibly corrupted.
The MQTT broker library
The library code has been moved to a separate repository at https://github.com/martin-ger/uMQTTBroker and is included recursivly.
It can be integrated into any NONOS SDK (or esp-open-sdk) program ("make -f Makefile.orig lib" will build the mqtt code as a C library). You can find a minimal NONOS SDK sample in the directory "user_basic" in this repository. Rename it to "user", adapt "user_config.h", and do the "make" to build a small demo that just starts an MQTT broker without any additional logic.
The broker is started by simply including:
#include "mqtt/mqtt_server.h"
and then calling
bool MQTT_server_start(uint16_t portno, uint16_t max_subscriptions, uint16_t max_retained_topics);
in the "user_init()" (or Arduino "setup()") function. Now it is ready for MQTT connections on all activated interfaces (STA and/or AP). Please note, that the lib uses two tasks (with prio 1 and 2) for client and broker. Thus, only task with prio 0 is left for a user application.
Limitations on the number of clients
To adjust memory consumption of one MQTT connection and thus the max number of concurrent connections you can redefine MQTT_BUF_SIZE and QUEUE_BUFFER_SIZE in "user_config.h". MQTT_BUF_SIZE is the max. size of pending inbound messages for one connection (and thus also the max. size of a single MQTT message) and QUEUE_BUFFER_SIZE is the max. size of all pending outbound messages for one connection. Currently these parameters are set to 1024 resp. 2048 bytes, resulting in a memory consumption of about 4 KB per connection and a max number of connections of about 8-9 (depending on the memory usage of the rest of the program). When you reduce buffer sizes, e.g. to 512 and 1024 bytes, a single connection requires only about 2.5 KB resulting in up to 13 possible concurrent MQTT connections. In any case you have to increase the number of TCP connections (default 5) first by calling "espconn_tcp_set_max_con(n)" with n, the max. number of concurrent TCP connections, less or equal to 15.
Also there is a hard limitation on the number of STAs connected to the SoftAP, which is 8. I.e. when using the esp_uMQTT_broker only with clients via the SoftAP interface, even with reduced memory consumtion, the limit of different client nodes is still 8, as it is imposed by the binary WiFi driver. Only when used via the STA interface and an external AP you can connect more than 8 MQTT clients.
Thanks
- pfalcon for esp_open_sdk (https://github.com/martin-ger/esp-open-sdk)
- tuanpmt for esp_mqtt (https://github.com/tuanpmt/esp_mqtt )
- eadf for esp8266_easygpio (https://github.com/eadf/esp8266_easygpio )
- Stefan Brüns for ESP8266_new_pwm (https://github.com/StefanBruens/ESP8266_new_pwm )
- Martin d'Allens for esphttpclient (https://github.com/Caerbannog/esphttpclient )
- Ian Craggs for mqtt_topic
- many others contributing to open software (for the ESP8266)