|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| components/pcap | ||
| main | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
| partitions_example.csv | ||
| sdkconfig.defaults | ||
| sniffer-example0-pcap.png | ||
README.md
Simple Sniffer Example
(See the README.md file in the upper level 'examples' directory for more information about examples.)
Overview
This example demonstrates basic usage of wifi sniffer mode by saving packets into SD card with pcap format. Go to wikipedia for more information about pcap.
This example is based on esp-idf's console component. For more information about console you should read this guide.
How to use example
Hardware Required
To run this example, you should have one ESP32 dev board integrated with a SD card slot (e.g ESP32-WROVER Kit) or just connect ESP32-DevKitC to a SD card breakout board.
Configure the project
Enter make menuconfig if you are using GNU Make based build system or enter idf.py menuconfig if you are using CMake based build system. Then go into Example Configuration menu.
- Check
Store command history in flashif you want to save command history into flash (recommend). - Set the mount point in your filesystem, for example,
/sdcardif you want to store pcap file into SD card. - Set the length of sniffer work queue.
- Set the stack size of the sniffer task.
- Set the priority of the sniffer task.
- Set the max number of packets to store in a single pcap file. The number of packets usually will be very large, so we just truncate them into multiple files. You should set a threshold value here.
Build and Flash
Enter make -j4 flash monitor if you are using GNU Make based build system or enter idf.py build flash monitor if you' are using CMake based build system.
(To exit the serial monitor, type Ctrl-].)
See the Getting Started Guide for full steps to configure and use ESP-IDF to build projects.
Example Output
sniffer Command Usage
sniffer [-f ][-i ] [-F <mgmt|data|ctrl|misc|mpdu|ampdu>]... [-c ][--stop] Capture specific packet and store in pcap format -f, --file= name of the file storing the packets in pcap format -i, --interface= which interface to capture packet -F, --filter=<mgmt|data|ctrl|misc|mpdu|ampdu> filter parameters -c, --channel= communication channel to use --stop stop running sniffer
The sniffer command support some important options as follow:
-f: Specify the name of file who will store the packets, default value issniffer, and the resulting file name will be like “snifferX.pcap”, here ‘X’ shows the file’s order.-i: Specify the interface to sniffer packets, currently only supportwlan-c:Specify the channel to sniffer packet-F: Specify the filter condition, currently only support following filter conditions, you can select any number of them- mgmt: Management packets
- data: Data packets
- ctrl: Control packets
- misc: Other packets
- mpdu: MPDU packets
- ampdu: AMPDU packets
--stop: Stop sniffer job
Mount SD Card
=======================================================
| Steps to sniffer WiFi packets |
| |
| 1. Enter 'help' to check all commands' usage |
| 2. Enter 'mount <device>' to mount filesystem |
| 3. Enter 'sniffer' to start capture packets |
| 4. Enter 'unmount <device>' to unmount filesystem |
| |
=======================================================
esp32> mount sd
I (158912) example: Initializing SD card
I (158912) example: Using SDMMC peripheral
I (158912) gpio: GPIO[13]| InputEn: 0| OutputEn: 1| OpenDrain: 0| Pullup: 0| Pulldown: 0| Intr:0
Name: SA16G
Type: SDHC/SDXC
Speed: 20 MHz
Size: 14832MB
Start Sniffer
esp32> sniffer -f sniffer-example -i wlan -c 2
I (36200) cmd_sniffer: Start WiFi Promicuous Mode
I (36270) phy: phy_version: 4000, b6198fa, Sep 3 2018, 15:11:06, 0, 0
I (36270) wifi: ic_enable_sniffer
I (36290) pcap: Store packets to file: /sdcard/sniffer-example0.pcap
I (103810) pcap: Close Pcap file OK
I (103830) pcap: Store packets to file: /sdcard/sniffer-example1.pcap
I (177300) pcap: Close Pcap file OK
I (177320) pcap: Store packets to file: /sdcard/sniffer-example2.pcap
esp32> sniffer --stop
I (212250) wifi: ic_disable_sniffer
I (212250) wifi: flush txq
I (212250) wifi: stop sw txq
I (212260) wifi: lmac stop hw txq
I (212340) pcap: Close Pcap file OK
I (212340) cmd_sniffer: Sniffer Stopped
Unmount SD Card
esp32> unmount sd
I (248800) example: Card unmounted
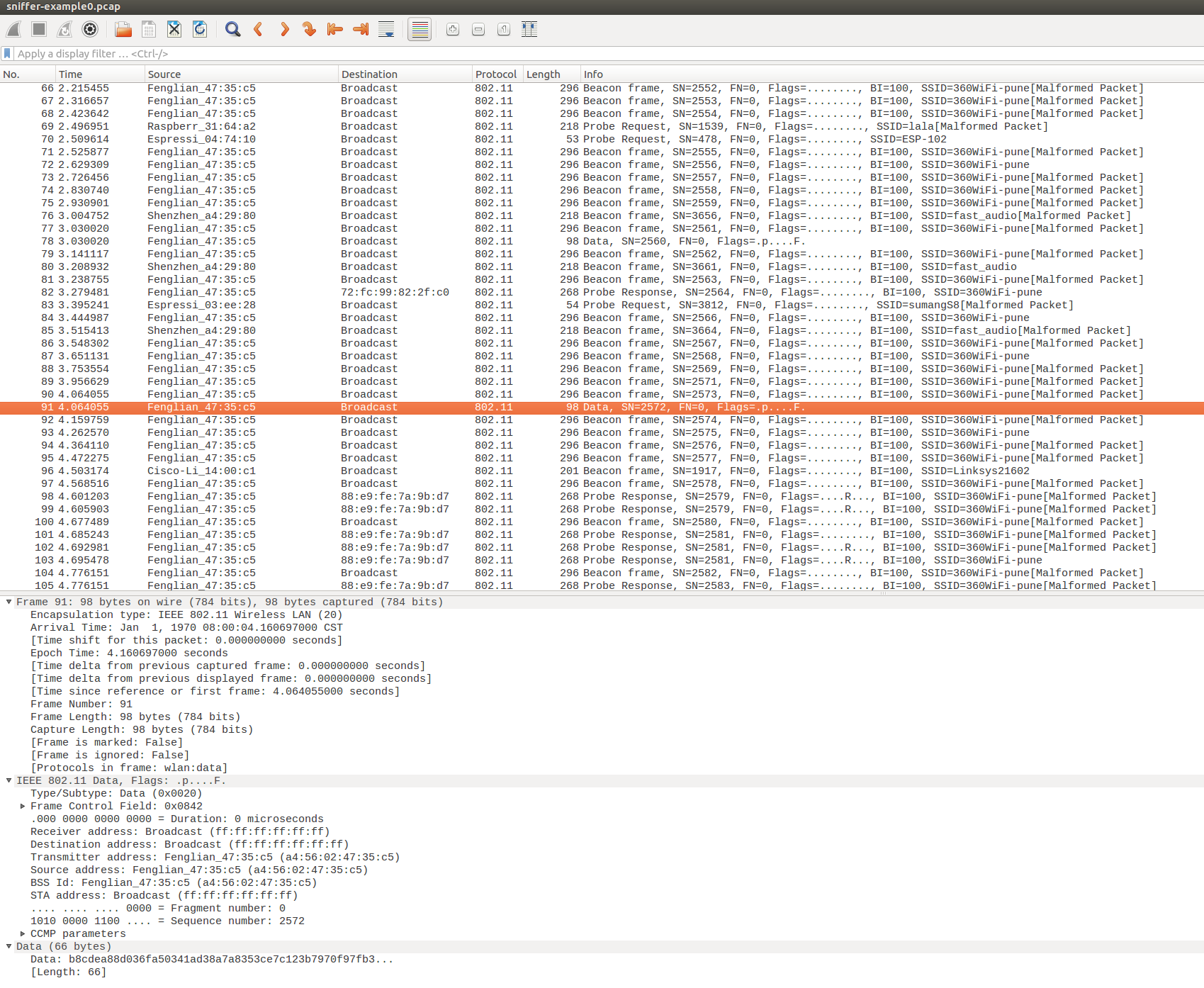
Open PCap File in Wireshark
Troubleshooting
- Make sure you have pluged in your SD card and mount it into filesystem before doing sniffer work or you will get error message like “Create file /sdcard/sniffer0.pcap failed”.
- To protect the SD card, we recommand you to execute command
unmount sdbefore you plug out your SD card.
(For any technical queries, please open an issue on GitHub. We will get back to you as soon as possible.)