kopia lustrzana https://github.com/kartoza/docker-postgis
rodzic
3db0328ee1
commit
55137f4418
|
|
@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ RUN chmod +x *.sh
|
|||
# Run any additional tasks here that are too tedious to put in
|
||||
# this dockerfile directly.
|
||||
RUN set -eux \
|
||||
&& /scripts/setup.sh
|
||||
&& /scripts/setup.sh;rm /scripts/.pass_*
|
||||
RUN echo 'figlet -t "Kartoza Docker PostGIS"' >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
VOLUME /var/lib/postgresql
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
35
README.md
35
README.md
|
|
@ -433,8 +433,9 @@ host / client):
|
|||
psql -h localhost -U docker -p 25432 -l
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** Default postgresql user is 'docker'. The password can be sourced withing
|
||||
the running container if you did not pass any env variable to explicitly set it.
|
||||
**Note:** Default postgresql user is 'docker'. If you do not pass
|
||||
the env variable `POSTGRES_PASS` a random strong password will be generated
|
||||
and can be accessed within the startup logs.
|
||||
|
||||
You can then go on to use any normal postgresql commands against the container.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -618,6 +619,10 @@ replicant is read-only.
|
|||
docker run --name "streaming-replication" -e REPLICATION=true -e WAL_LEVEL='replica' -d -p 25432:5432 kartoza/postgis:13.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** If you do not pass the env variable `REPLICATION_PASS` a random password
|
||||
will be generated and will be visible from the logs or within the container in
|
||||
`/tmp/REPLPASSWORD.txt`
|
||||
|
||||
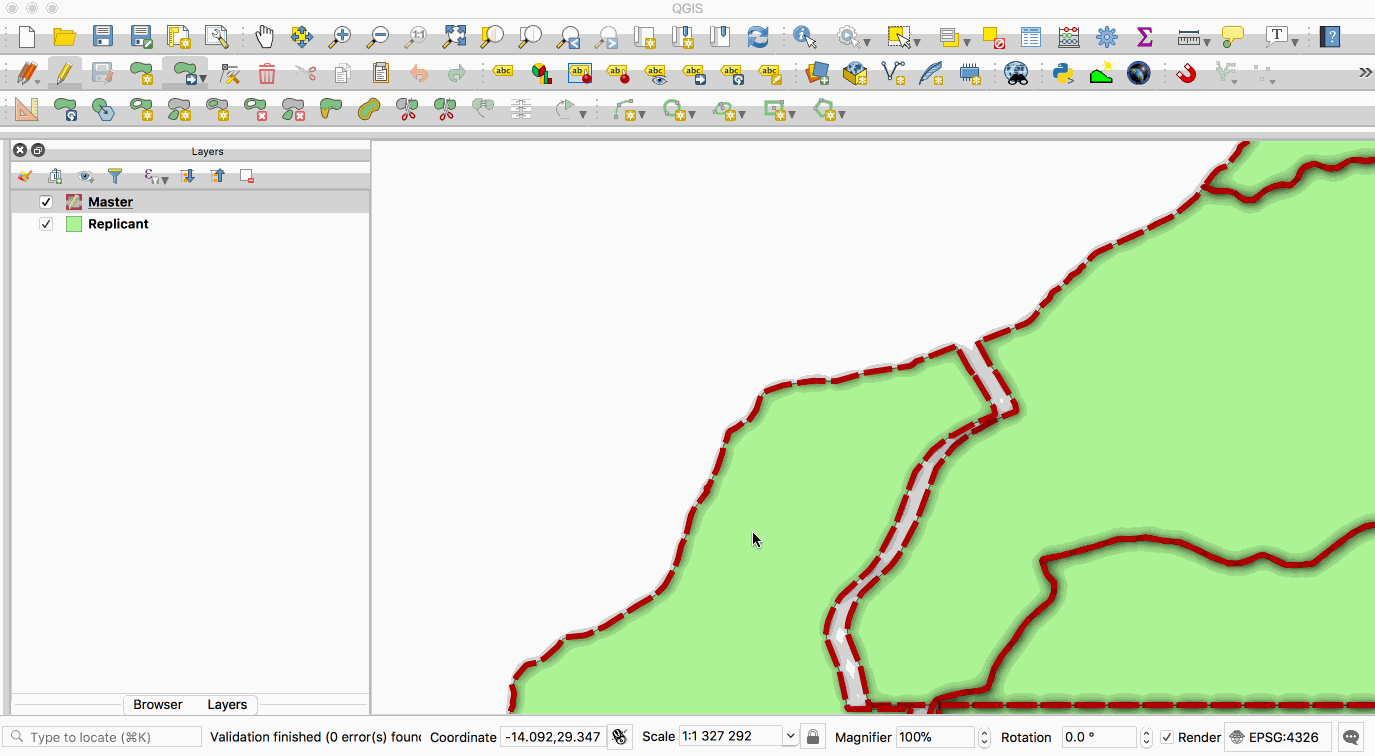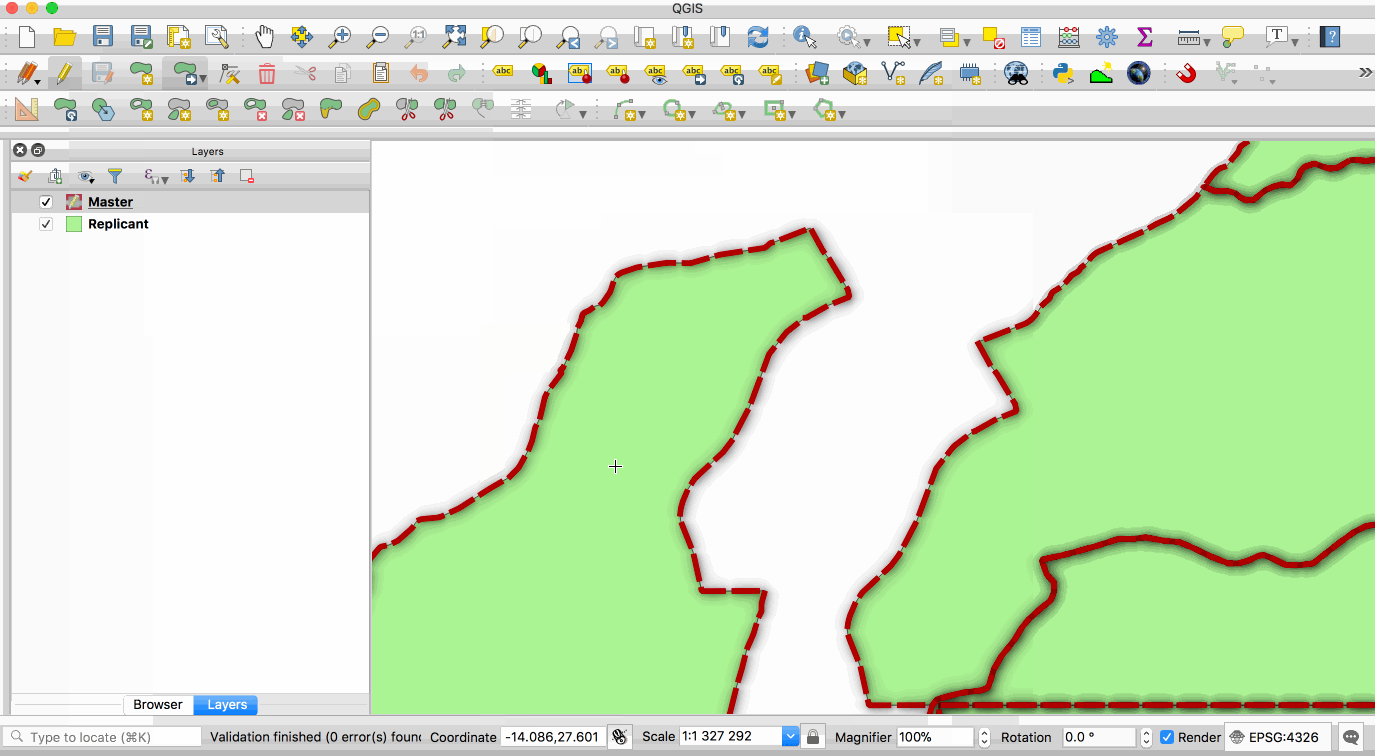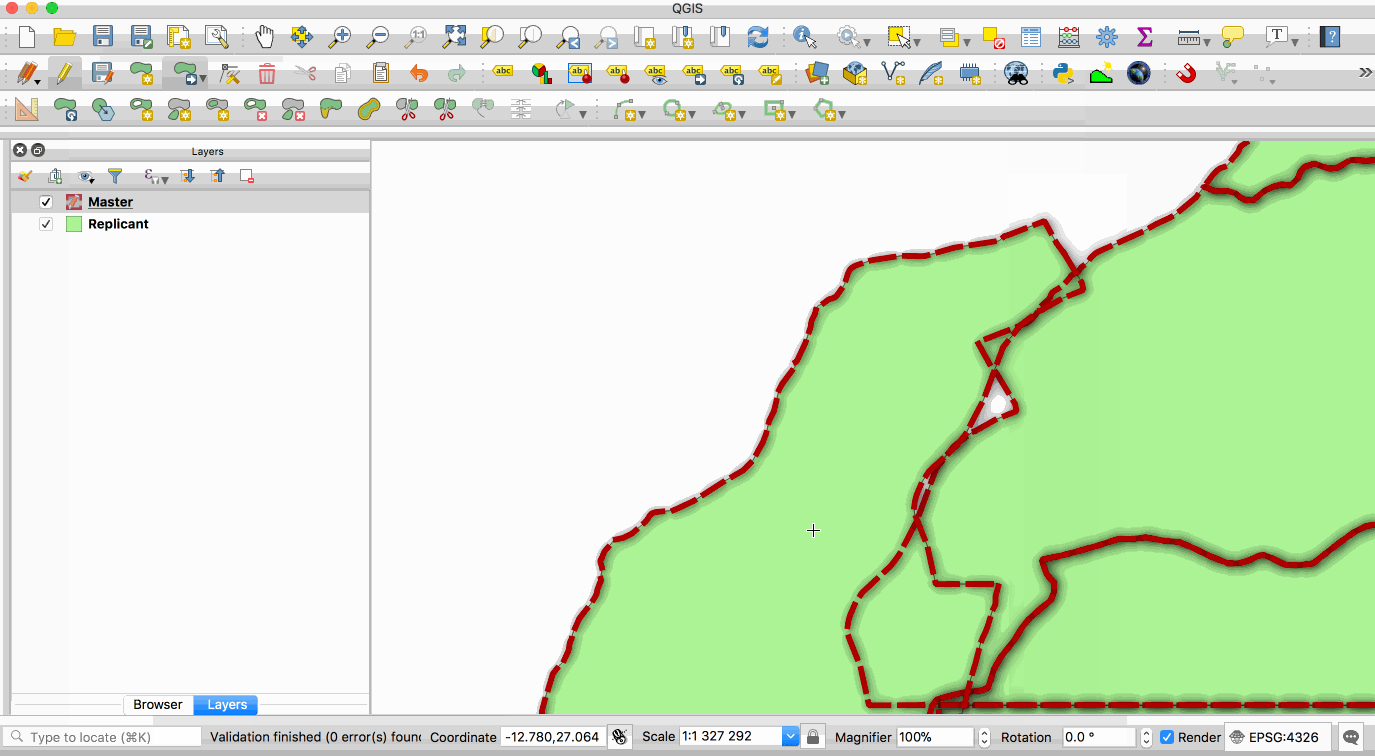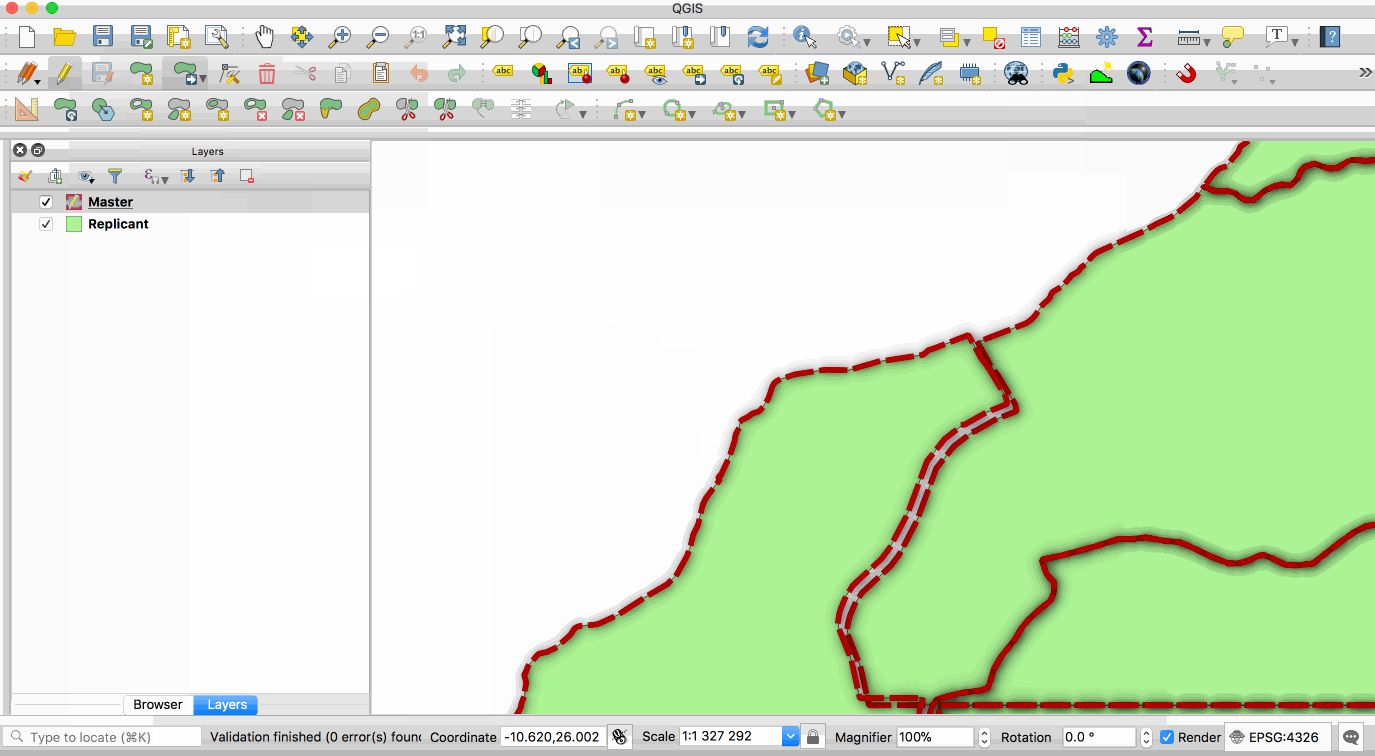
|
||||
|
||||
This image is provided with replication abilities. We can
|
||||
|
|
@ -628,6 +633,20 @@ mirror database content from a designated master. This replication scheme allows
|
|||
us to sync databases. However, a `replicant` is only for read-only transaction, thus
|
||||
we can't write new data to it. The whole database cluster will be replicated.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Database permissions
|
||||
|
||||
Since we are using a role ${REPLICATION_USER}, we need to ensure that it has access to all
|
||||
the tables in a particular schema. So if a user adds another schema called `data`
|
||||
to the database `gis` he also has to update the permission for the user
|
||||
with the following SQL assuming the ${REPLICATION_USER} is called replicator
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA data GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO replicator;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**NB** You need to set up a strong password for replication otherwise the
|
||||
default password for ${REPLICATION_USER} will default to `replicator`
|
||||
|
||||
To experiment with the replication abilities, you can see a [docker-compose.yml](sample/replication/docker-compose.yml)
|
||||
sample. There are several environment variables that you can set, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -719,7 +738,7 @@ into slave environment and set `DESTROY_DATABASE_ON_RESTART: 'False'`.
|
|||
|
||||
After this, you can make changes to your replicant, but master and replicant will not
|
||||
be in sync anymore. This is useful if the replicant needs to take over a failover master.
|
||||
However, it is recommended to take additional action, such as creating a backup from the
|
||||
However it is recommended to take additional action, such as creating a backup from the
|
||||
slave so a dedicated master can be created again.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Preventing replicant database destroy on restart
|
||||
|
|
@ -729,7 +748,7 @@ to prevent the database from being destroyed on restart. With this setting you c
|
|||
shut down your replicant and restart it later and it will continue to sync using the existing
|
||||
database (as long as there are no consistencies conflicts).
|
||||
|
||||
However, you should note that this option doesn't mean anything if you did not
|
||||
However, you should note that this option doesn't mean anything if you didn't
|
||||
persist your database volume. Because if it is not persisted, then it will be lost
|
||||
on restart because docker will recreate the container.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -740,12 +759,12 @@ To activate the following you need to use the environment variable
|
|||
`WAL_LEVEL=logical` to get a running instance like
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run --name "logical-replication" -e REPLICATION=true -e WAL_LEVEL=logical -d kartoza/postgis:14-3.1
|
||||
docker run --name "logical-replication" -e WAL_LEVEL=logical -d kartoza/postgis:13.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For a detailed example see the docker-compose in the folder `sample/logical_replication`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker image versions
|
||||
### Docker image versions
|
||||
|
||||
All instructions mentioned in the README are valid for the latest running image.
|
||||
Other docker images might have a few missing features than the ones in the
|
||||
|
|
@ -755,10 +774,10 @@ in the latest tagged version of the image are essential for the previous image
|
|||
you can cherry-pick the changes against that specific branch and we will
|
||||
test and merge.
|
||||
|
||||
## Support
|
||||
### Support
|
||||
|
||||
If you require more substantial assistance from [kartoza](https://kartoza.com) (because our work and interaction on docker-postgis is pro bono),
|
||||
please consider taking out a [Support Level Agreement](https://kartoza.com/en/shop/product/support)
|
||||
please consider taking out a [Support Level Agreeement](https://kartoza.com/en/shop/product/support)
|
||||
|
||||
## Credits
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,9 +17,21 @@ source /scripts/setup-pg_hba.sh
|
|||
# Function to add figlet
|
||||
figlet -t "Kartoza Docker PostGIS"
|
||||
|
||||
POSTGRES_PASS=$(cat /tmp/PGPASSWORD.txt)
|
||||
echo -e "[Entrypoint] GENERATED Postgres PASSWORD: \e[1;31m $POSTGRES_PASS"
|
||||
echo -e "\033[0m PGPASSWORD Generated above: "
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ -f /scripts/.pass_20.txt ]]; then
|
||||
USER_CREDENTIAL_PASS=$(cat /scripts/.pass_20.txt)
|
||||
cp /scripts/.pass_20.txt /tmp/PGPASSWORD.txt
|
||||
echo -e "[Entrypoint] GENERATED Postgres PASSWORD: \e[1;31m $USER_CREDENTIAL_PASS"
|
||||
echo -e "\033[0m PGPASSWORD Generated above: "
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ -f /scripts/.pass_22.txt ]]; then
|
||||
USER_CREDENTIAL_PASS=$(cat /scripts/.pass_22.txt)
|
||||
cp /scripts/.pass_22.txt /tmp/REPLPASSWORD.txt
|
||||
echo -e "[Entrypoint] GENERATED Replication PASSWORD: \e[1;34m $USER_CREDENTIAL_PASS"
|
||||
echo -e "\033[0m Replication password Generated above: "
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ -z "$REPLICATE_FROM" ]]; then
|
||||
# This means this is a master instance. We check that database exists
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -72,6 +72,14 @@ then
|
|||
fi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function generate_random_string() {
|
||||
STRING_LENGTH=$1
|
||||
random_pass_string=$(openssl rand -base64 ${STRING_LENGTH})
|
||||
if [[ ! -f /scripts/.pass_${STRING_LENGTH}.txt ]]; then
|
||||
echo ${random_pass_string} > /scripts/.pass_${STRING_LENGTH}.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
export RAND=$(cat /scripts/.pass_${STRING_LENGTH}.txt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Make sure we have a user set up
|
||||
if [ -z "${POSTGRES_USER}" ]; then
|
||||
|
|
@ -79,6 +87,12 @@ if [ -z "${POSTGRES_USER}" ]; then
|
|||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -z "${POSTGRES_PASS}" ]; then
|
||||
generate_random_string 20
|
||||
POSTGRES_PASS=${RAND}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -z "${POSTGRES_DBNAME}" ]; then
|
||||
POSTGRES_DBNAME=gis
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
|
@ -255,6 +269,10 @@ if [ -z "${REPLICATION_USER}" ]; then
|
|||
REPLICATION_USER=replicator
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -z "${REPLICATION_PASS}" ]; then
|
||||
generate_random_string 22
|
||||
REPLICATION_PASS=${RAND}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -z "$IGNORE_INIT_HOOK_LOCKFILE" ]; then
|
||||
IGNORE_INIT_HOOK_LOCKFILE=false
|
||||
|
|
@ -336,7 +354,7 @@ function restart_postgres {
|
|||
kill_postgres
|
||||
|
||||
# Brought postgres back up again
|
||||
source /env-data.sh
|
||||
source /scripts/env-data.sh
|
||||
su - postgres -c "$SETVARS $POSTGRES -D $DATADIR -c config_file=$CONF &"
|
||||
|
||||
# wait for postgres to come up
|
||||
|
|
@ -411,27 +429,4 @@ until su - postgres -c "${PG_BASEBACKUP} -X stream -h ${REPLICATE_FROM} -p ${REP
|
|||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function pg_password() {
|
||||
SETUP_LOCKFILE="/settings/.pgpasspass.lock"
|
||||
if [ -z "${POSTGRES_PASS}" ] && [ ! -f ${SETUP_LOCKFILE} ]; then
|
||||
POSTGRES_PASS=$(openssl rand -base64 15)
|
||||
touch ${SETUP_LOCKFILE}
|
||||
echo "$POSTGRES_PASS" > /tmp/PGPASSWORD.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "$POSTGRES_PASS" > /tmp/PGPASSWORD.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function replication_password() {
|
||||
SETUP_LOCKFILE="/settings/.replicationpass.lock"
|
||||
if [ -z "${REPLICATION_PASS}" ] && [ ! -f ${SETUP_LOCKFILE} ]; then
|
||||
REPLICATION_PASS=$(openssl rand -base64 15)
|
||||
touch ${SETUP_LOCKFILE}
|
||||
echo "$REPLICATION_PASS" > /tmp/REPLPASSWORD.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "$REPLICATION_PASS" > /tmp/REPLPASSWORD.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
|
|||
|
||||
source /scripts/env-data.sh
|
||||
|
||||
POSTGRES_PASS=$(cat /tmp/PGPASSWORD.txt)
|
||||
INITDB_WALDIR_FLAG=""
|
||||
|
||||
# Check POSTGRES_INITDB_WALDIR value
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,8 +7,6 @@ if [ -f "${SETUP_LOCKFILE}" ]; then
|
|||
return 0
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup Postgresql password
|
||||
pg_password
|
||||
|
||||
# This script will setup pg_hba.conf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,9 +15,6 @@ source /scripts/env-data.sh
|
|||
# Only create credentials if this is a master database
|
||||
# Slave database will just mirror from master users
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
POSTGRES_PASS=$(cat /tmp/PGPASSWORD.txt)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check user already exists
|
||||
echo "Creating superuser $POSTGRES_USER"
|
||||
RESULT=`su - postgres -c "psql postgres -t -c \"SELECT 1 FROM pg_roles WHERE rolname = '$POSTGRES_USER'\""`
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,8 +24,6 @@ if [ -z "$RESULT" ]; then
|
|||
fi
|
||||
su - postgres -c "psql postgres -c \"$COMMAND USER $POSTGRES_USER WITH SUPERUSER ENCRYPTED PASSWORD '$POSTGRES_PASS';\""
|
||||
|
||||
replication_password
|
||||
REPLICATION_PASS=$(cat /tmp/REPLPASSWORD.txt)
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Creating replication user $REPLICATION_USER"
|
||||
RESULT_REPLICATION=`su - postgres -c "psql postgres -t -c \"SELECT 1 FROM pg_roles WHERE rolname = '$REPLICATION_USER'\""`
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Ładowanie…
Reference in New Issue