|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| SuperBuild | ||
| contrib | ||
| docker | ||
| docs | ||
| hooks | ||
| img | ||
| licenses | ||
| modules | ||
| opendm | ||
| stages | ||
| tests | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| CNAME | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| VERSION | ||
| code_of_conduct.md | ||
| configure.sh | ||
| configure_18_04.sh | ||
| odm_docker_readme.txt | ||
| portable.Dockerfile | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| run.py | ||
| run.sh | ||
| settings.yaml | ||
| start-dev-env.sh | ||
| test.sh | ||
README.md
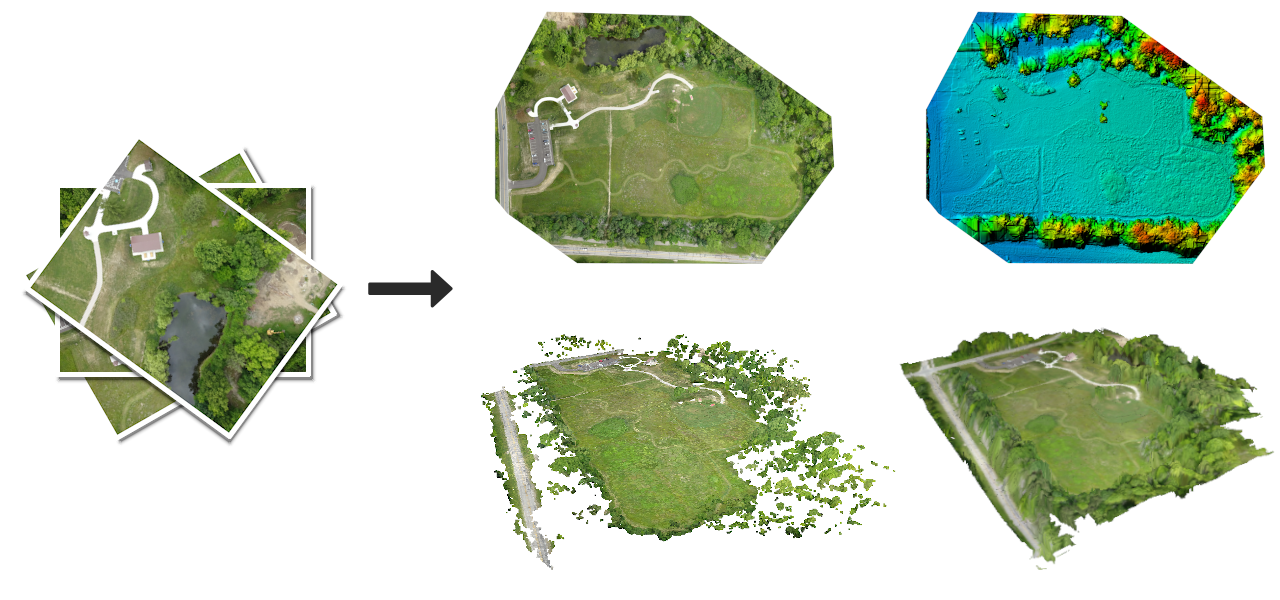
An open source command line toolkit for processing aerial drone imagery. ODM turns simple 2D images into:
- Classified Point Clouds
- 3D Textured Models
- Georeferenced Orthorectified Imagery
- Georeferenced Digital Elevation Models
The application is available for Windows, Mac and Linux and it works from the command line, making it ideal for power users, scripts and for integration with other software.
If you would rather not type commands in a shell and are looking for a friendly user interface, check out WebODM.
Quickstart
The easiest way to run ODM is via docker. To install docker, see docs.docker.com. Once you have docker installed and working, you can run ODM by placing some images (JPEGs or TIFFs) in a folder named “images” (for example C:\Users\youruser\datasets\project\images or /home/youruser/datasets/project/images) and simply run from a Command Prompt / Terminal:
# Windows
docker run -ti --rm -v c:/Users/youruser/datasets:/datasets opendronemap/odm --project-path /datasets project
# Mac/Linux
docker run -ti --rm -v /home/youruser/datasets:/datasets opendronemap/odm --project-path /datasets project
You can pass additional parameters by appending them to the command:
docker run -ti --rm -v /datasets:/datasets opendronemap/odm --project-path /datasets project [--additional --parameters --here]
For example, to generate a DSM (--dsm) and increase the orthophoto resolution (--orthophoto-resolution 2) :
docker run -ti --rm -v /datasets:/datasets opendronemap/odm --project-path /datasets project --dsm --orthophoto-resolution 2
Viewing Results
When the process finishes, the results will be organized as follows:
|-- images/
|-- img-1234.jpg
|-- ...
|-- opensfm/
|-- see mapillary/opensfm repository for more info
|-- odm_meshing/
|-- odm_mesh.ply # A 3D mesh
|-- odm_texturing/
|-- odm_textured_model.obj # Textured mesh
|-- odm_textured_model_geo.obj # Georeferenced textured mesh
|-- odm_georeferencing/
|-- odm_georeferenced_model.laz # LAZ format point cloud
|-- odm_orthophoto/
|-- odm_orthophoto.tif # Orthophoto GeoTiff
You can use the following free and open source software to open the files generated in ODM:
- .tif (GeoTIFF): QGIS
- .laz (Compressed LAS): CloudCompare
- .obj (Wavefront OBJ), .ply (Stanford Triangle Format): MeshLab
Note! Opening the .tif files generated by ODM in programs such as Photoshop or GIMP might not work (they are GeoTIFFs, not plain TIFFs). Use QGIS instead.
API
ODM can be made accessible from a network via NodeODM.
Documentation
See http://docs.opendronemap.org for tutorials and more guides.
Forum
We have a vibrant community forum. You can search it for issues you might be having with ODM and you can post questions there. We encourage users of ODM to partecipate in the forum and to engage with fellow drone mapping users.
Native Install (Ubuntu 16.04)
You can run ODM natively on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (although we don't recommend it):
- Download the source from here
- Run
bash configure.sh install - Download a sample dataset from here (about 550MB) and extract it in
/datasets/aukerman - Run
./run.sh --project-path /datasets odm_data_aukerman
Updating a native installation
When updating to a newer version of ODM, it is recommended that you run
bash configure.sh reinstall
to ensure all the dependent packages and modules get updated.
Build From Source
If you want to rebuild your own docker image (if you have changed the source code, for example), from the ODM folder you can type:
docker build -t my_odm_image --no-cache .
When building your own Docker image, if image size is of importance to you, you should use the --squash flag, like so:
docker build --squash -t my_odm_image .
This will clean up intermediate steps in the Docker build process, resulting in a significantly smaller image (about half the size).
Experimental flags need to be enabled in Docker to use the --squash flag. To enable this, insert the following into the file /etc/docker/daemon.json:
{
"experimental": true
}
After this, you must restart docker.
Developers
Help improve our software! We welcome contributions from everyone, whether to add new features, improve speed, fix existing bugs or add support for more cameras. Check our code of conduct, the contributing guidelines and how decisions are made.
For Linux users, the easiest way to modify the software is to make sure docker is installed, clone the repository and then run from a shell:
$ DATA=/path/to/datasets ./start-dev-env.sh
Where /path/to/datasets is a directory where you can place test datasets (it can also point to an empty directory if you don't have test datasets).
Run configure to set up the required third party libraries:
(odmdev) [user:/code] master+* ± bash configure.sh reinstall
You can now make changes to the ODM source. When you are ready to test the changes you can simply invoke:
(odmdev) [user:/code] master+* ± ./run.sh --project-path /datasets mydataset
If you have questions, join the developer's chat at https://community.opendronemap.org/c/developers-chat/21
- Try to keep commits clean and simple
- Submit a pull request with detailed changes and test results
- Have fun!